Integration of Education
ISSN (print): 1991-9468, ISSN (online): 2308-1058
Founder and publisher: National Research Ogarev Mordovia State University
Editor-in-Chief: Dmitriy E. Glushko, Cand.Sci. (Ped.)
Frequency / Access: 4 issues per year / Open
Included in: White list (1st level), Higher Attestation Commission List, RISC, RSCI, Scopus
Website: https://edumag.mrsu.ru
Integration of Education – a peer-reviewed open-access scholarly journal. The journal Integration of Education publishes original scientific articles (Full Articles) in Russian and English, previously not published in other editions. The aim of the journal is an objective presentation of results of original scientific research of current leading tendencies of educational processes, analysis of pedagogical, psychological and sociological problems of education development in Russia and the international scientific community.
The journal’s mission is to maintain and develop a unified research space in the field of education integration, as well as to foster interuniversity cooperation of academic staff.
The journal is addressed to researchers, analysts and practitioners in the field of pedagogy, psychology and sociology of education, as well as to a wide range of readers interested in the problems of integrating education in modern society.
The Editorial Board reviews (double-blind review) all incoming papers. The manuscript of the article is sent for review to several leading specialists of the corresponding profile, who have scientific specialization closest to the subject of the article, to evaluate the scientific content.
The Editorial Board follows the principle of zero tolerance to plagiarism. Plagiarism сhecking is carried out by using Anti-Plagiarism and iThenticate software.
The journal adheres to editorial ethics standards following international practice of editing, reviewing, publishing and authorship of scientific publications and recommendations of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
The journal is distributed in Russia and other countries of the world.
The journal offers direct open access to full-text issues based on the following principle: open access to research results contributes to the increase of global knowledge sharing.
The Journal is included in the List of peer reviewed scientific journals published by the Higher Attestation Commission in which major research results from the dissertations of Candidates of Sciences (Cand.Sci.) and Doctor of Science (Dr.Sci.) degrees are to be published. Scientific specialties of dissertations and their respective branches of science are as follows:
- Pedagogical psychology, psychodiagnostics of digital educational environments (psychological sciences),
- Social structure, social institutions and processes (sociological sciences),
- Sociology of culture (sociological sciences),
- Sociology of management (sociological sciences),
- General pedagogy, history of pedagogy and education (pedagogical sciences),
- Theory and methods of training and education (by fields and levels of education) (pedagogical sciences),
- Correctional pedagogy (surdopedagogy and typopedagogy, oligophrenopedagogy and speech therapy) (pedagogical sciences),
- Methodology and technology of professional education (pedagogical sciences).
最新一期
卷 29, 编号 4 (2025)
- 年: 2025
- ##issue.datePublished##: 18.12.2025
- 文章: 9
- URL: https://bakhtiniada.ru/1991-9468/issue/view/20356
完整期次
International Experience in the Integration of Education
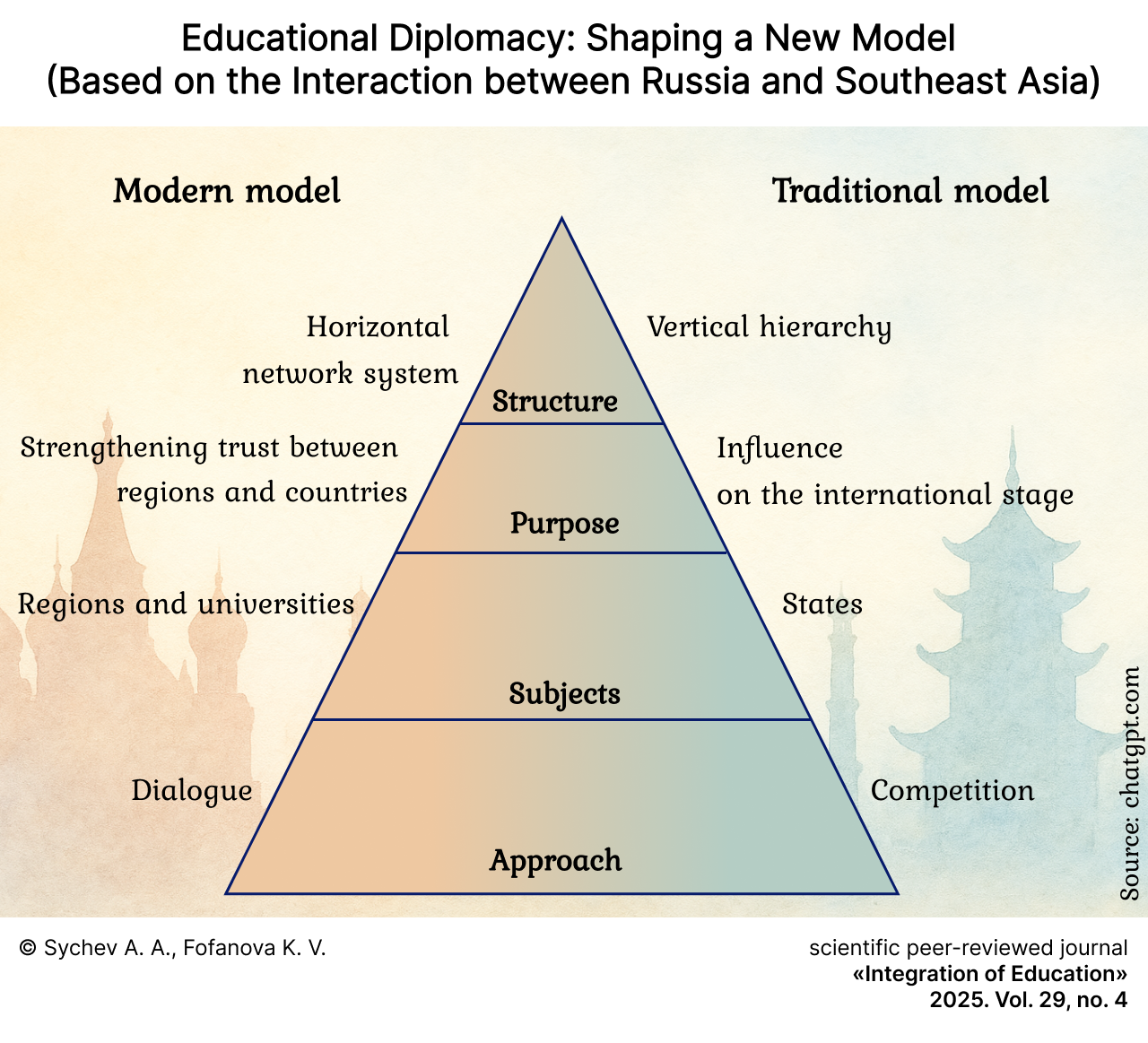
Educational Diplomacy: Shaping a New Model (Based on the Interaction between Russia and Southeast Asia)
摘要
Introduction. Russia’s active participation in international education programs and its presence in the educational spaces of several regions of Southeast Asia (India, Laos, China) are exhausting the heuristic potential of traditional theoretical approaches to educational diplomacy. Therefore, a rethinking of the goals, means, motives, and actors of educational diplomacy is required in light of contemporary conditions and challenges. The aim of this study is to conceptualize the potential of educational diplomacy in the context of cultural interaction between Russian regions and Southeast Asian countries.
Materials and Methods. The article is based on the results of the authors’ research conducted in March – May 2025 using semi-formalized expert interviews. The experts (15 people) were members of the academic community in Russia, India, Laos, France, and Taiwan. The methods used made it possible to consider the problems of educational diplomacy from different points of view, which made it possible to identify the features of the modern model of educational diplomacy.
Results. A comparison of two systems of educational diplomacy was made: traditional and modern. The main factors influencing the nature and content of educational diplomacy were identified. Internal incentives arising from the logic of academic development and the ethos of scientific activity are particularly important for the modern model. Recommendations are given on how to improve the effectiveness of educational diplomacy in the new sociocultural conditions, which concern the optimization of international activities in the field of education, including the need to develop cultural competencies, involve local residents more widely in teaching Russian language and culture, and create certification programs and distance learning courses for teachers at foreign universities.
Discussion and Conclusion. The study revealed that a new model of educational diplomacy is currently emerging, based on networking at the regional and university levels and driven by the internal educational and research needs of universities. This article will be useful to academics involved in international educational activities, specialists in regional policy, and diplomatic personnel.
 610-625
610-625


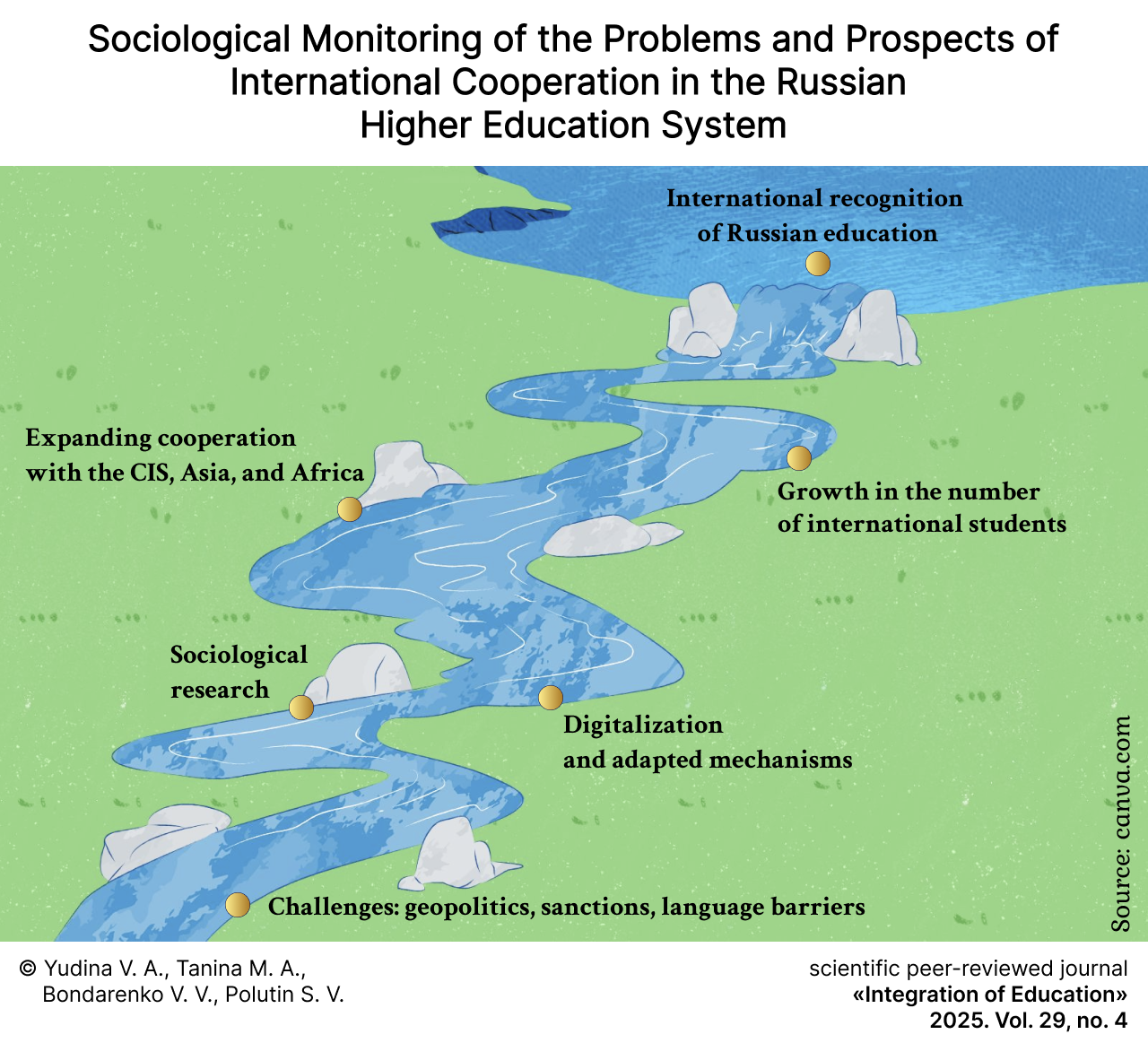
Sociological Monitoring of the Problems and Prospects of International Cooperation in the Russian Higher Education System
摘要
Introduction. In the context of ongoing geopolitical and institutional transformations within the global educational sphere, there is an urgent need to develop adaptive mechanisms for international educational collaboration. These mechanisms must integrate digital distance technologies designed to advance Russian higher education offerings in the international market for educational services. Nevertheless, current academic literature offers insufficient detail regarding how international cooperation in higher education influences: the transformation of educational program content and competencies; the employment prospects, mobility, and professional trajectories of international graduates; and the quality assurance systems shaped by various accreditation standards. This research aims to analyze the current approaches to the digitalization and internationalization of higher education, assess the preparedness of the Russian higher education system for integrating digital distance technologies across its research, educational, and international communication functions, and ultimately, formulate recommendations for enhancing existing international cooperation frameworks.
Materials and Methods. The empirical research was conducted in 2025 using an online survey of 183 respondents. These individuals held various positions related to international activities and work with international students in Russian universities, representing 69 regions across all federal districts of the country. A comprehensive set of scientific cognition methods, including content analysis and sociological surveys, was employed to identify a range of problems and trends in the implementation of international educational cooperation amidst the digitalization of higher education. Adaptive mechanisms for international educational cooperation were developed using statistical and structural-logical research techniques.
Results. A theoretical analysis of statistical and analytical materials from domestic and international organizations and experts enabled the formulation of trends in the digitalization and internationalization of higher education, the proposal of adaptive mechanisms for implementing international educational cooperation, and the outlining of their development prospects. Based on the empirical findings, two key groups of problems in the implementation of international cooperation within the Russian higher education system (internal and external) were identified, and their resolution pathways were developed.
Discussion and Conclusion. The conclusions and recommendations formulated by the authors contribute to the development of methodological frameworks for adapting international educational cooperation mechanisms. These adaptations are designed to address the complexities arising from geopolitical and geo-economic instability, and to meet the evolving requirements of higher education digitalization and internationalization. This article’s findings are expected to be beneficial for experts engaged in research on improving the efficacy of exports within the higher education services sector. Furthermore, they will be of particular interest to university leadership teams aiming to enhance their strategies for attracting international students and cultivating partnerships with overseas entities in diverse fields of collaboration.
 626-644
626-644


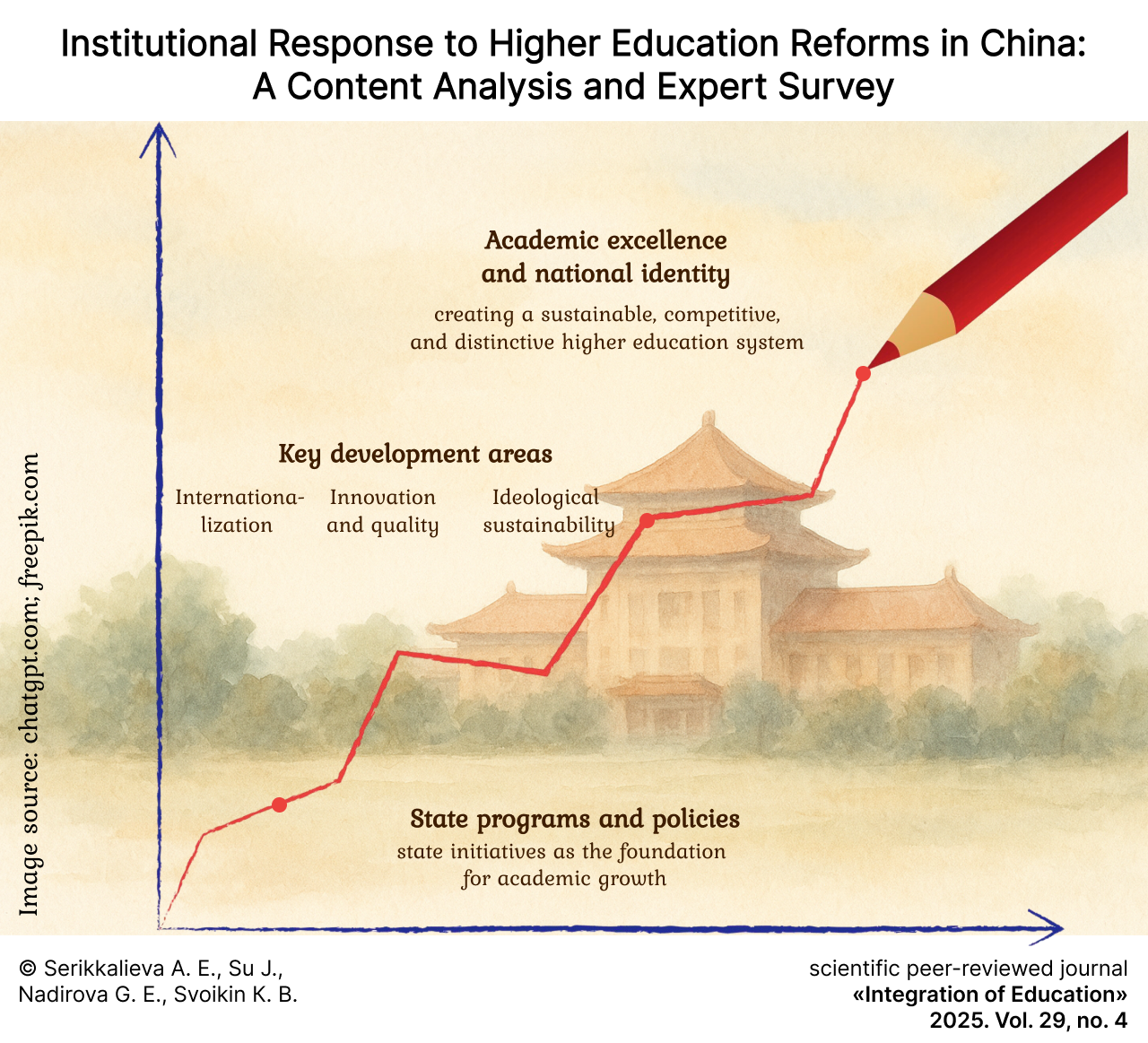
Institutional Response to Higher Education Reforms in China: A Content Analysis and Expert Survey
摘要
Introduction. Global competition is prompting governments in many countries to implement large-scale reforms to improve the competitiveness of their universities. In response, China is implementing long-term programs to achieve academic excellence, reflecting a unique model of educational modernization. Despite a significant number of studies on the issue of reform, their perception by the Chinese university community has not been sufficiently researched. The aim of this study is to examine the perception of educational reforms by university faculty and administrators based on an analysis of documents and expert opinions.
Materials and Methods. As part of the study, a survey was conducted among 68 experts representing universities, teacher training colleges, schools, and educational institutions of various levels, including central and regional organizations related to China’s higher education system. An in-depth interpretation of the results and verification of the identified trends were carried out through an analysis of regulatory acts and policy statements by the senior leadership of the PRC on the development of higher education. A content analysis was conducted to track changes in rhetoric in official documents from different years. At the final stage, empirical data were compared with the results of the content analysis, which ensured the integrity and validity of the research conclusions.
Results. The expert survey confirmed that many priorities of state programs correspond to actual changes in universities. Teachers and administrators generally give a positive assessment of the reforms that have been implemented. Key success factors have been identified: systematic implementation of state plans, strict control of education quality, and development of university infrastructure throughout the country. Respondents noted the importance of targeted government funding for leading universities and cooperation between universities and corporations. Among the practical priorities for change, experts highlighted the introduction of innovative educational technologies, the development of practice-oriented programs, and the expansion of international cooperation at the institutional level. The evolution of reform goals from a focus on foreign models and internationalization to an emphasis on domestic scientific schools and the ideological framing of education as a national paradigm is demonstrated.
Discussion and Conclusion. China’s experience of modernizing higher education represents a unique model that combines the strategic goal of achieving global scientific excellence with the preservation of national identity and strict centralized management. The authors’ conclusions contribute to the development of understanding of the institutional mechanisms of universities’ adaptation to state reforms in the field of higher education in China.
 645-665
645-665


Pedagogical Psychology
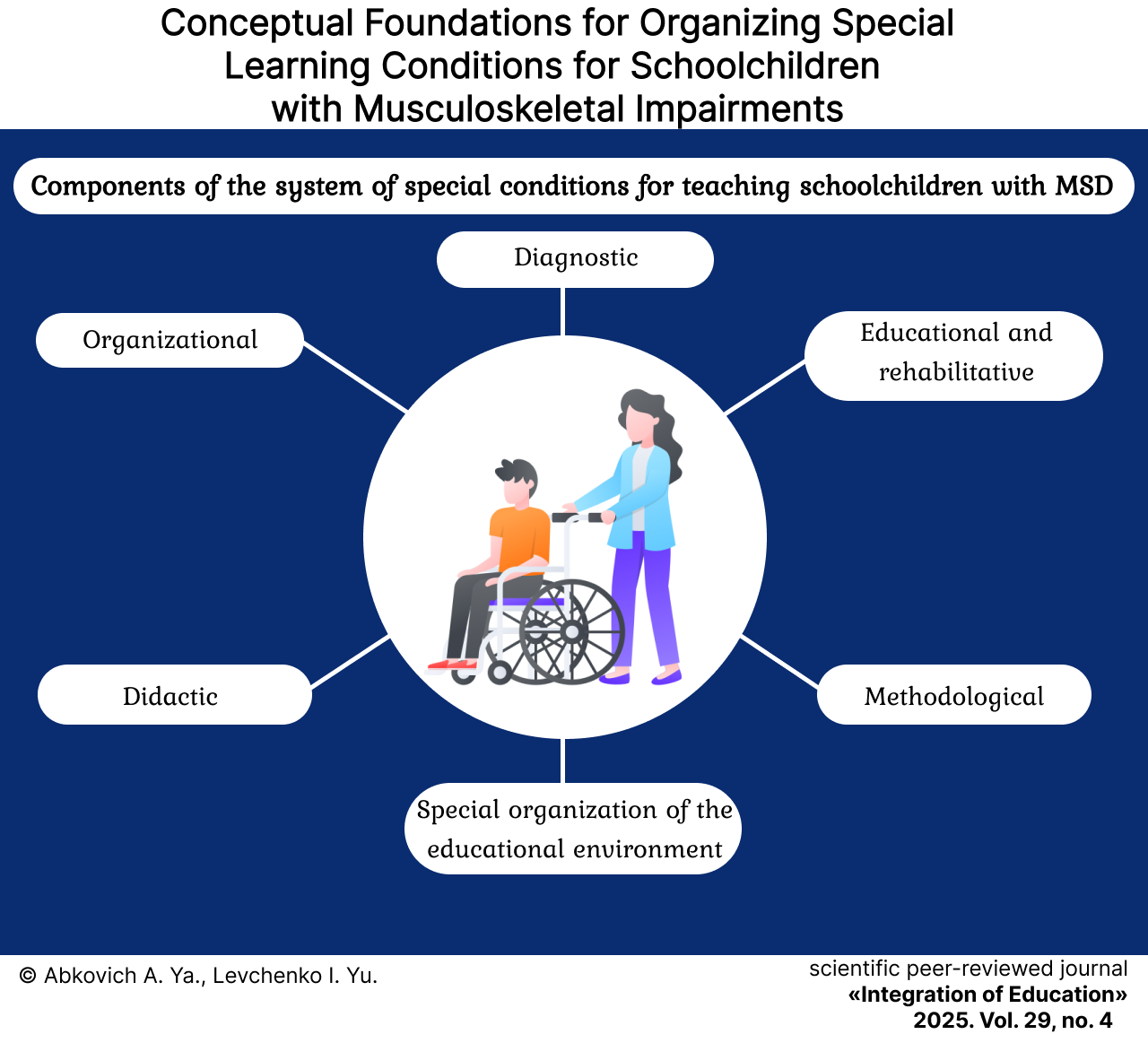
Conceptual Foundations for Organizing Special Learning Conditions for Schoolchildren with Musculoskeletal Impairments
摘要
Introduction. The transformation of the school education system for children with musculoskeletal impairments, driven by changes in public life and legislation, is a response to the social demand for the quality and accessibility of education for children with disabilities and special educational needs. However, there is a lack of research focused on the qualitative peculiarities of the development of modern children with motor impairments, their specific educational needs, and the conditions necessary for their successful learning. The aim of the study is to develop a system of special learning conditions for schoolchildren with musculoskeletal impairments.
Materials and Methods. The design of the system for special learning conditions for schoolchildren with musculoskeletal impairments was based on an analysis of specialized literature on the research problem, a study of the clinical, psychological, and pedagogical characteristics of the current population of children with motor pathologies (n = 842), their specific educational needs, and the results of monitoring special learning conditions conducted through a survey of educators from 319 educational organizations. Methods used to study the developmental characteristics and specific needs of children with motor impairments included analysis of medical data, psychological and pedagogical experiments, observation, interviews, and methods of mathematical and descriptive statistics.
Results. Conceptual foundations for a system of special learning conditions for schoolchildren with musculoskeletal impairments have been developed. The goal of organizing this system is to enhance the quality and accessibility of general education for students by creating optimal conditions for their development, education, and social adaptation. The conceptual framework consists of humanistic, systemic, complex, level-based, individually oriented and subject-subject approaches. The system is based on the variable educational needs of schoolchildren, which are determined based on their individual typological characteristics, and provide a level-based organization of special conditions in schools (basic, advanced and optimal levels). Each of the levels corresponds to the school's preparedness to learn and meet the special educational needs of a certain group of students with musculoskeletal impairments.
Discussion and Conclusion. The research resulted in a tiered system for organizing special learning conditions for students with musculoskeletal impairments. An approach is proposed where a school’s preparedness to educate children with musculoskeletal impairments is viewed as a real characteristic of preparedness to educate children with motor pathologies and diverse educational needs, determined by considering the specific educational needs of individual students within a particular school. The article’s materials contain new data on the phenomenology and structure of the special educational needs of schoolchildren with motor impairments and approaches to their implementation. These findings will be useful for researchers and practicing educators in the field of special and inclusive education.
 666-683
666-683


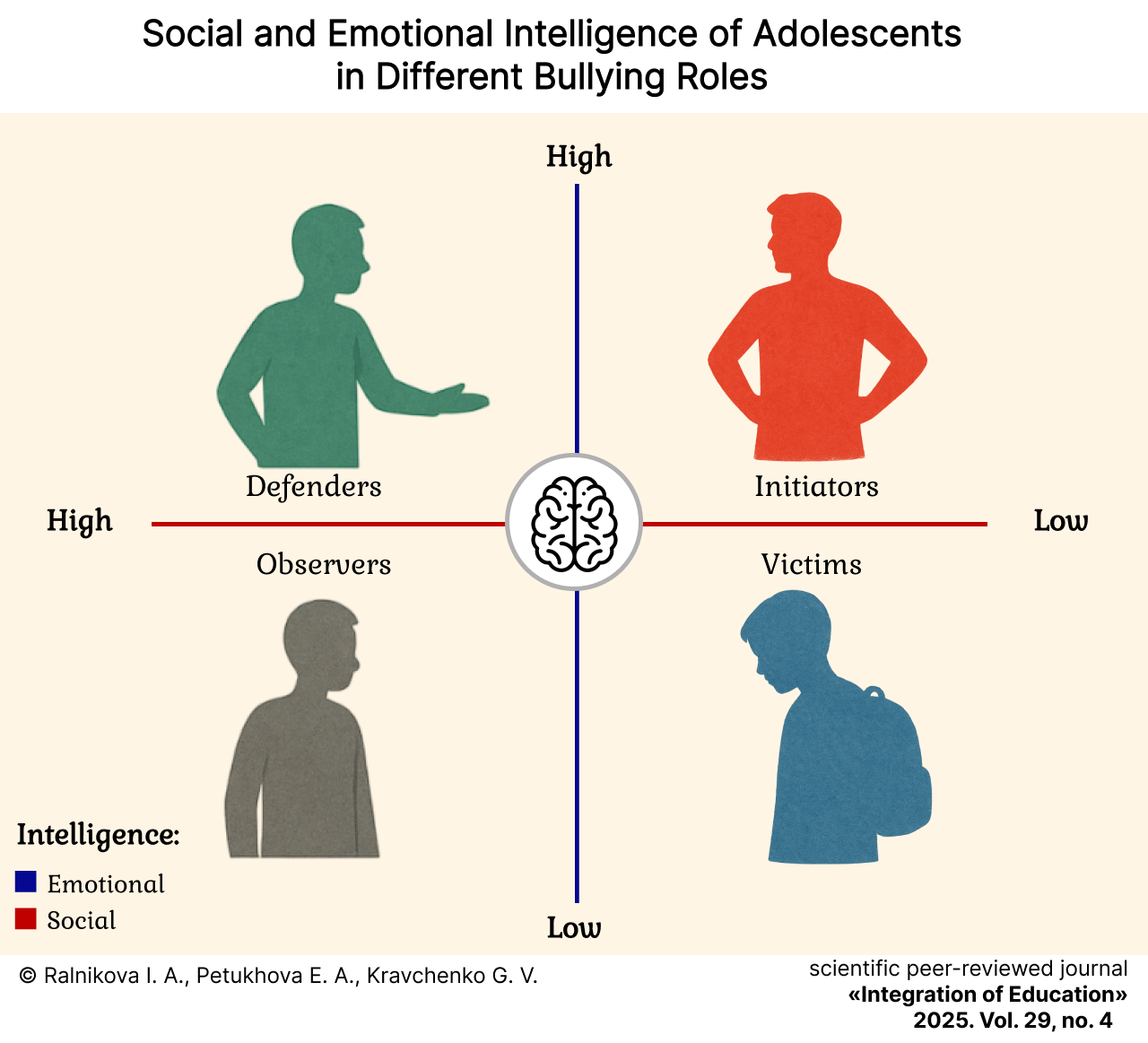
Social and Emotional Intelligence of Adolescents in Different Bullying Roles
摘要
Introduction. School bullying significantly impacts the learning and upbringing processes of contemporary adolescents. The problem of school bullying has been extensively and substantively examined through the lens of educational psychology and pedagogical psychology. However, a systematic understanding of this issue from the perspective of the factors contributing to the emergence and functioning of bullying, and the study of social and emotional intelligence characteristics as factors influencing students’ involvement in bullying, remain relevant. The aim of the study is to investigate the characteristics of social and emotional intelligence in adolescents with different roles in the bullying process.
Materials and Methods. The study involved 252 secondary school students (53% girls and 47% boys) aged 14–15 years. The “bullying structure” identification method (E.G. Norkina) was used to define roles in bullying. The “Self-Regulation and Interpersonal Communication Success” methodology (V.N. Kunitsyna) was employed to determine social intelligence characteristics. The emotional intelligence questionnaire (D.V. Lyusin) was used to assess adolescents’ perceptions of their own emotional intelligence. Statistically significant differences between adolescent samples were established using the Kruskal – Wallis non-parametric test.
Results. Differences in social and emotional intelligence have been revealed among adolescents who play the roles of initiator, victim, defender, and observer in school bullying. Teenagers who are victims of bullying are more spontaneous and open in communication, more adapted to situations of communication and successful in it, compared with initiators, defenders and observers. Initiators, defenders, and observers are better able than victims to recognize and identify the emotions of others, understand their causes, possible consequences, and manage them.
Discussion and Conclusion. The research findings indicate the necessity of a differentiated approach to pedagogical interaction and the provision of psycho-corrective assistance to adolescents involved in bullying, depending on their role and considering the development of social and emotional intelligence. The proposed materials may be useful for teachers, educational psychologists, psychologists, and social educators.
 684-697
684-697


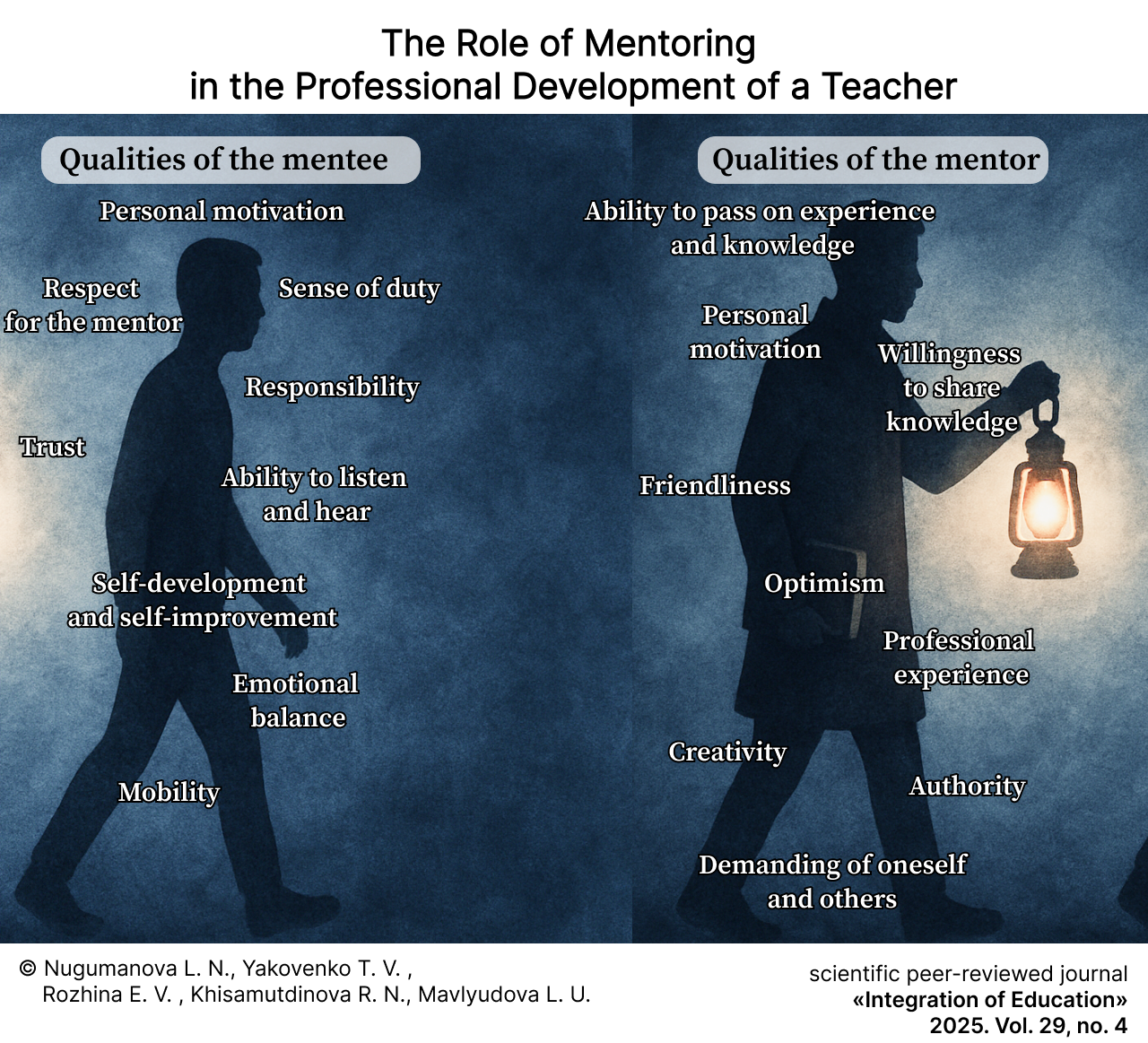
The Role of Mentoring in the Professional Development of a Teacher
摘要
Introduction. Mentoring is an important element of the continuing professional education system, ensuring the continuous professional development and improvement of teachers. In the context of rapid changes in the educational environment, the introduction of digital technologies, the updating of federal state educational standards, and growing demands on the quality of teaching, the role of mentoring is becoming particularly important. The aim of the study is to identify and analyze the motivation of mentors to participate in mentoring programs, as well as to systematize the factors that determine the effectiveness of the mentoring process.
Materials and Methods. The study involved 321 teachers from various educational organizations, which ensured the representativeness of the data and allowed for a comparison based on level of experience. Quantitative and qualitative data on teachers’ perceptions of the mentoring system were obtained using a hybrid questionnaire combining closed and open questions, rating scales, and demographic indicators. Significant correlations between professional experience, participation in mentoring programs, and perceived effectiveness were identified using mathematical statistics methods (mean values, standard deviations, correlation coefficients, percentage distribution).
Results. Teachers consider mentoring to be an effective tool for professional development, contributing to the growth of competencies, personal improvement, and the strengthening of the professional community. Representatives of the middle age group reported the highest satisfaction with mentoring activities, which indicates a harmonious combination of experience and motivation to transfer knowledge. The effectiveness of mentoring is largely determined by the personal qualities of the mentor–responsibility, diligence, respect for their mentees, and internal motivation. At the same time, social recognition and support for mentors remain important conditions for the successful implementation of mentoring programs.
Discussion and Conclusion. The study empirically confirmed the high significance of mentoring as an effective mechanism for professional development and the transfer of pedagogical experience. The practical significance of the work lies in the possibility of using the data obtained to improve mentoring models, develop methodological recommendations, and professional development programs for teaching staff. Prospects for further research are related to an in-depth analysis of the influence of mentors’ personal and professional characteristics on the effectiveness of interaction, as well as the development of diagnostic tools and digital models of mentoring processes. The results obtained are of interest to researchers in the field of pedagogy, specialists in the system of additional professional education, and heads of educational organizations.
 698-710
698-710


Monitoring of Education
Matrimonial Strategies of Regional Youth: Typology, Dispositions, Dynamics
摘要
Introduction. Effective matrimonial strategies are the foundation for demographic indicators and a prerequisite for achieving national project outcomes, while their transformation creates risks and prospects for the reproduction of national human capital. Despite numerous demographic publications, research focusing on the systematic and comprehensive study of changes in youth matrimonial strategies in relation to the dynamics of the social situation is lacking. The objective of this study is to assess the characteristics of matrimonial strategies of social groups within regional youth and the dynamics of indicators in the context of a frontline border region.
Materials and Methods. The analytical basis of this article is derived from data of “Social Strategies of Youth” monitoring (2021–2023) and the results of the “Matrimonial Strategies of Youth” study (2024). The research was conducted using a stratified quota sample, with districts of the Belgorod Region serving as the groups. Quota criteria included gender, age, and settlement type of respondents. Broad participant coverage within a short timeframe was achieved through online surveys conducted via recruiters. The “hot recruiting” technique involves recruiters working on sample recruitment using the “snowball sampling” method, with targeted dissemination of information about the ongoing work and individual consultation for respondents on research questions.
Results. Problems related to risky indicators of non-obligatory childbearing in the 18–21 year old youth group have been identified. Despite the connection between the matrimonial dispositions of regional youth and the priority of family and its values, this position solidifies with age, highlighting the significant role of educational institutions in mitigating demographic risks. Problematic issues concerning gender emphases in matrimonial dispositions and choices have been formulated, demonstrating a lesser orientation towards family and childbearing among young women compared to men. Risks of the devaluation of family values and the diminished significance of matrimonial plans for youth with low economic income have been identified.
Discussion and Conclusion. The results of the study contribute to the development of sociology of youth and sociology of the family. The research materials may be of interest to state youth policy management bodies at various levels, state and municipal administration bodies, youth organizations, and educational institutions.
 711-733
711-733


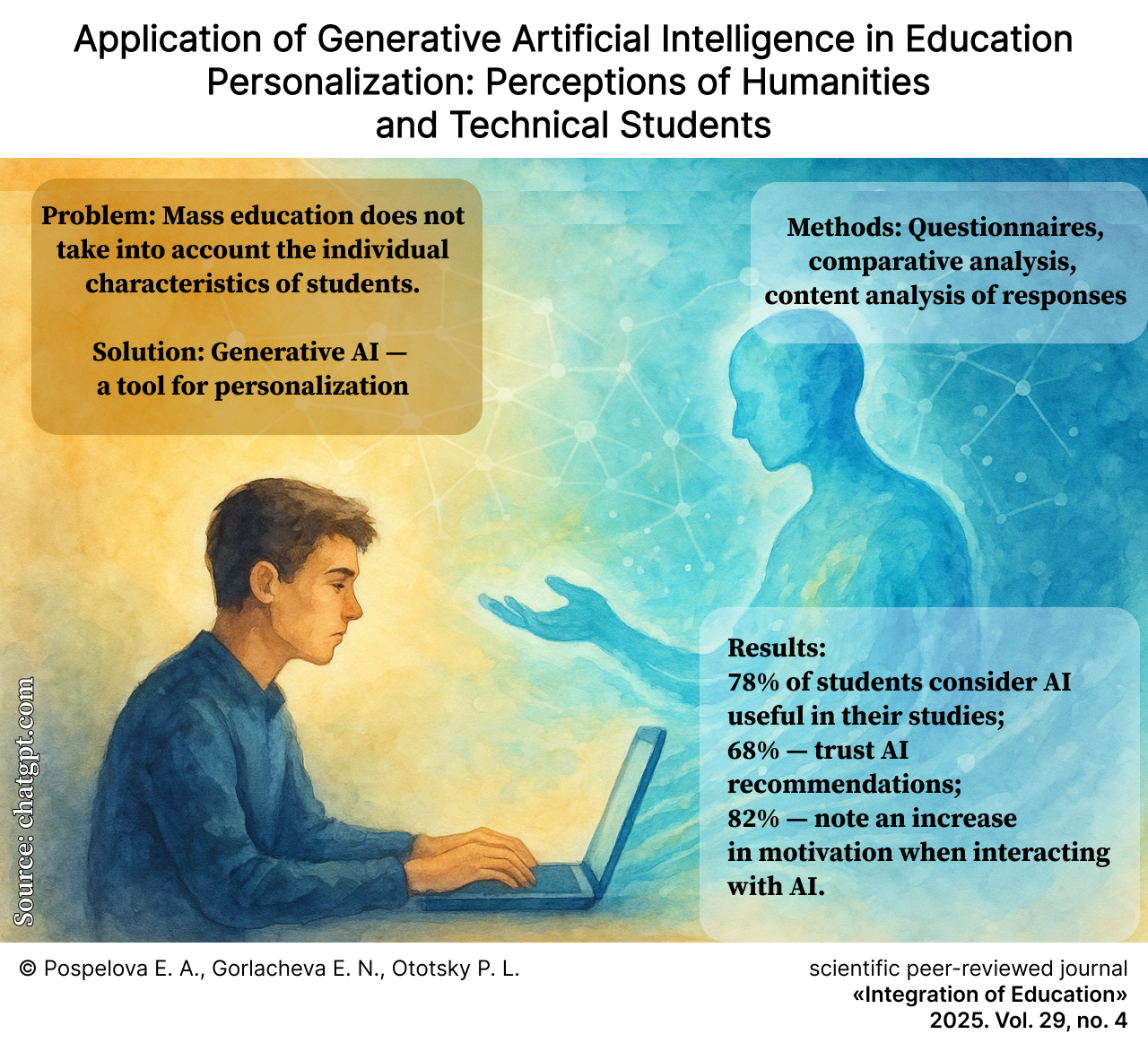
Application of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Education Personalization: Perceptions of Humanities and Technical Students
摘要
Introduction. The intensive integration of generative artificial intelligence technologies has led to significant transformations across various fields, including education. The expansive development of information technologies has enabled the simplification of education personalization, enhancing its quality, accessibility, and methodological diversity. The advantages of these new technologies compel the scientific community to seek effective methods and approaches for applying artificial intelligence in learning and to anticipate upcoming changes in the educational environment. The aim of this study is to examine the experience of humanities and technical students using chatbots and to analyze students’ perceptions of educational process personalization through artificial intelligence.
Materials and Methods. The empirical basis comprises data from a sociological survey conducted from June 2024 to January 2025, involving 730 undergraduate and graduate students from Russian universities. The survey was administered via online questionnaires designed to test the formulated scientific hypotheses.
Results. The findings demonstrate a positive attitude among students towards the systematic implementation of artificial intelligence in the educational process and the utilization of personalized learning elements (digital mentors and chatbots) that foster improved interaction and support during learning. Negative sentiments were identified among students regarding the use of artificial intelligence for assessing their academic performance, indicating insufficient trust in the objectivity and accuracy of such technologies in evaluation. The necessity for further analysis and the development of strategies for the effective integration of artificial intelligence into the educational environment, taking into account student needs and concerns, is emphasized. Notably, the perceptions of humanities and technical students differ only slightly.
Discussion and Conclusion. The theoretical and methodological provisions developed in this article complement existing approaches and tools for studying the impact of modern technologies on the educational process. The conclusions drawn by the authors can be utilized by university administrators and government bodies for developing strategies for artificial intelligence application in education. Additionally, the results may be of value to curriculum designers and methodologists seeking to employ artificial intelligence in the development of learner-centered courses, where students are central to the educational process and their opinions are key in creating individualized learning paths.
 734-752
734-752


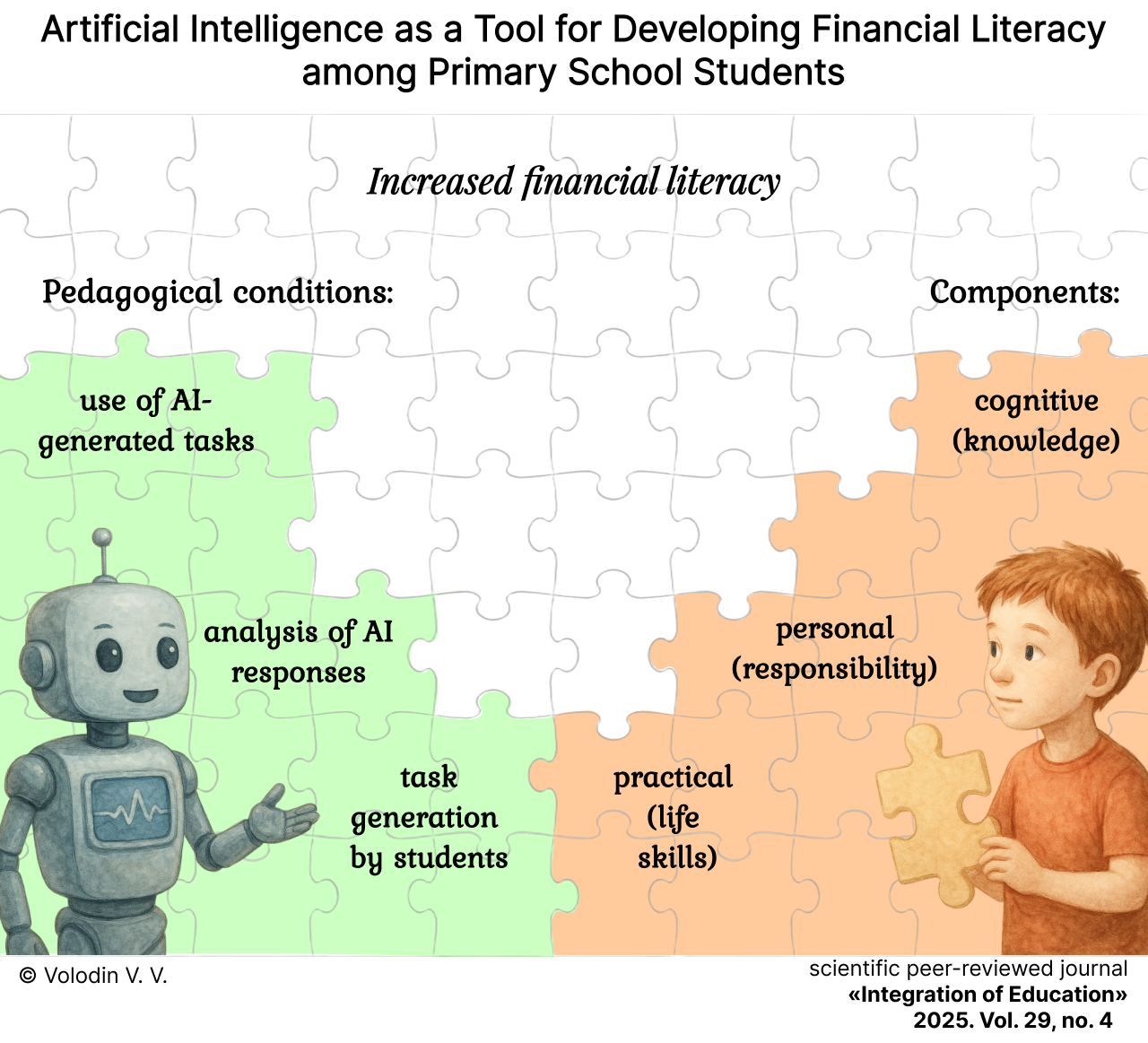
Artificial Intelligence as a Tool for Developing Financial Literacy among Primary School Students
摘要
Introduction. The state policy aimed at improving the financial literacy of the population, the rapid digitalization of education, and the increasing role of artificial intelligence in teaching primary school students underscore the relevance of this research. However, the problem of forming financial literacy in primary school students through artificial intelligence technologies has not been a subject of special study. The aim of the research is to develop pedagogical conditions for the use of artificial intelligence as a tool for forming financial literacy in primary school students.
Materials and Methods. Experimental work was conducted at two schools in the Amur Region. The sample included 122 third-grade primary school students, divided into two experimental and two control groups. Financial literacy was analyzed using diagnostic tools developed by S.V. Surikova and Yu.A. Nikolskaya. Statistical differences in the formation of financial literacy among participants were assessed using the non-parametric Mann – Whitney U-test.
Results. Pedagogical conditions for the use of artificial intelligence have been developed, the implementation of which ensures the formation of cognitive, personal, and practical components of financial literacy in students. The use of tasks that enrich students’ knowledge of finances and financial and economic relations contributes to the development of skills in applying basic financial concepts in various life situations (cognitive component). The formation of responsibility for financial decisions is facilitated by students’ analysis of artificial intelligence outputs (personal component). Engaging primary school students in generating tasks using artificial intelligence stimulates their development of skills for making informed purchases and savings and for independent planning of ways to achieve financial goals (practical component).
Discussion and Conclusion. The research contributes to educational practice regarding the development of financial literacy among primary school students through the application of artificial intelligence technologies. The article’s materials can be useful for primary school teachers in the process of fostering financial literacy in students. Future research prospects include the search for alternative pedagogical conditions and the development of a model for forming financial literacy in primary school students through artificial intelligence technologies.
 753-767
753-767