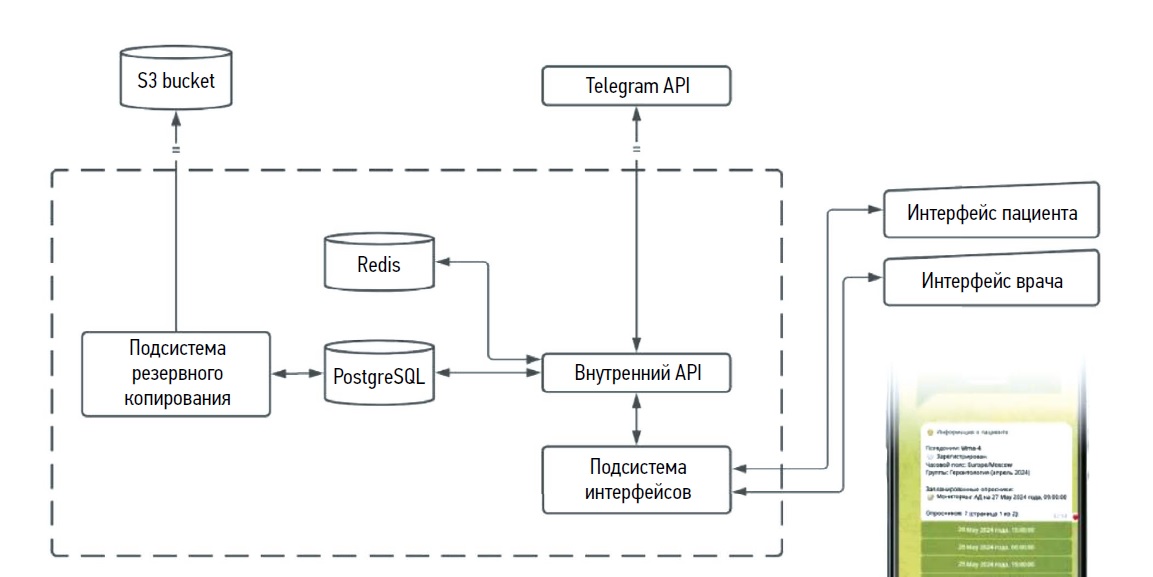
利用个人聊天软件平台对类风湿性关节炎患者进行远程监测
- 作者: Prokofeva Y.A.1, Belenkov Y.N.1, Kozhevnikova M.V.1, Zheleznykh E.A.1, Alborova Z.V.1, Menshikova I.V.1
-
隶属关系:
- Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
- 期: 卷 5, 编号 4 (2024)
- 页面: 740-751
- 栏目: 原创性科研成果
- URL: https://bakhtiniada.ru/DD/article/view/309833
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD634074
- ID: 309833
如何引用文章
详细
论证。远程医疗技术是在疾病诊断、治疗和后续康复过程中,监测患者的一种很有前景的方法。在本文中,作者对类风湿关节炎患者的远程监测和治疗控制的数字工具有效性与临床实践的融合进行了研究。
目的 — 评估使用远程监控平台对类风湿性关节炎患者进行监测的安全性、有效性和技术特点。
材料和方法。这项前瞻性非随机对照研究,纳入了出院接受门诊随访的18岁以上,患有严重和中度活动性类风湿关节炎患者。患者分为两组:远程监测和面对面监测。远程评估患者病情的数据是通过个人聊天软件平台 “Telemedbot”的患者监测软件包进行问卷调查获得的。同时,作者还使用了HAQ问卷来评估类风湿关节炎患者的日常生活能力;欧洲生活质量问卷EQ-5D;评估患者对建议的遵守情况、晨僵持续时间、疼痛和肿胀关节数量的问题;用于整体疾病评估的视觉模拟量表。6个月后,使用DAS28指数对两组患者的类风湿关节炎疗效进行评估。
结果。30名患者参加了为期6个月的远程监测计划。 面对面监测组也有30名患者。6个月后,使用个人聊天软件平台“Telemedbot”的患者中,类风湿关节炎的低活动度和病情缓解高于第二组(p=0.049)。在远程监测组中,分别有9名(30.0%)和11名(36.7%) 患者获得缓解,且疾病活动度较低,而面对面对照组中分别有 3名(10.0%)和8名(26.7%) 患者获得缓解。因此,在远程监测组中,有20人(66.7%)成功控制了疾病,而在面对面监测组中,只有11人(36.7%)能够控制病情。
结论。使用个人聊天软件平台“Telemedbot”进行远程监控可以被认为是提高医疗服务的可用性和类风湿性关节炎治疗有效性的潜在工具。
作者简介
Yuliya A. Prokofeva
Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
编辑信件的主要联系方式.
Email: ulyaprokofeva@gmail.com
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-8658-3435
SPIN 代码: 3545-2640
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow
Yuri N. Belenkov
Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: belenkov_yu_n@staff.sechenov.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-3014-6129
SPIN 代码: 5661-4691
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), academician member of the Russian Academy of Sciences
俄罗斯联邦, MoscowMaria V. Kozhevnikova
Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: kozhevnikova_m_v@staff.sechenov.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-4778-7755
SPIN 代码: 8501-9812
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow
Elena A. Zheleznykh
Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: zheleznykh_e_a@staff.sechenov.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-2596-192X
SPIN 代码: 2941-4875
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine)
俄罗斯联邦, MoscowZarina V. Alborova
Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: Zari.Alborova2002@yandex.ru
ORCID iD: 0009-0004-6090-4922
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow
Irina V. Menshikova
Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: menshikova_i_v@staff.sechenov.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-3181-5272
SPIN 代码: 5373-7486
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow参考
- Erdes ShF. Definition of the term «Rheumatology»: do we need this and how do the eular and the acr look at this? Rheumatology Science and Practice. 2018;56(3):389–390. (In Russ.) doi: 10.14412/1995-4484-2018-389-390
- Solomon DH, Rudin RS. Digital health technologies: opportunities and challenges in rheumatology. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 2020;16:525–535. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0461-x
- Kim OT, Dadaeva VA, Telkhigova AA, Drapkina OM. Mobile medical applications: opportunities, challenges and prospects. Russian Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2021;24(7):96–102. (In Russ.) doi: 10.17116/profmed20212407196
- Clinical guidelines — Rheumatoid arthritis. ID: KR250. Approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. 2021. Available from: https://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/402775973/ (In Russ.)
- Venuturupalli RS, Sufka P, Bhana S. Digital Medicine in Rheumatology. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America. 2019;45(1):113–126. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2018.09.010
- Black RJ, Cross M, Haile LM, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis, 1990–2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet Rheumatology. 2023;5(10):e594–e610. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00211-4
- Karateev AE, Polishchuk EY, Makhmudov HR, et al. How Russian patients with rheumatoid arthritis assess their condition: initial data from the OPTIMA (Patient Assessment of Severity, Outcomes and Medical Care in Arthritis) pilot study. Modern Rheumatology Journal. 2023;17(6):65–71. (In Russ.) doi: 10.14412/1996-7012-2023-6-65-71
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JW, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2010;69(4):631–637. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.123919
- Combe B, Landewe R, Daien CI, et al. 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of early arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2017;76(6):948–959. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210602
- Stoffer MA, Schoels MM, Smolen JS, et al. Evidence for treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: results of a systematic literature search update. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2016;75(5):16–22. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207526corr1
- Schett G, Emery P, Tanaka Y, et al. Tapering biologic and conventional DMARD therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: current evidence and future directions. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2016;75(8):1428–1437. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209201
- Nasonov EL, Olyunin YuA, Lila AM. Rheumatoid Arthritis: the Problems of Remission and Therapy Resistance. Rheumatology Science and Practice. 2018;56(3):263–271. (In Russ.) doi: 10.14412/1995-4484-2018-263-271
- Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bergstra SA, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2023;82(3):3–18. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223356corr1
- De Thurah A, Bosch P, Marques A, et al. 2022 EULAR points to consider for remote care in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2022;81(8):1065–1071. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2022-222341
- Marques A, Bosch P, de Thurah A, et al. Effectiveness of remote care interventions: a systematic review informing the 2022 EULAR Points to Consider for remote care in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. RMD Open. 2022;8(1):e002290. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002290
- Luo D, Wang P, Lu F, et al. Mobile Apps for Individuals With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. JCR: Journal of Clinical Rheumatology. 2019;25(3):133–141. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000800
- Gandrup J, Ali SM, McBeth J, et al. Remote symptom monitoring integrated into electronic health records: A systematic review. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. 2020;27(11):1752–1763. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa177
- Nikiphorou E, Santos EJF, Marques A, et al. 2021 EULAR recommendations for the implementation of self-management strategies in patients with inflammatory arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2021;80(10):1278–1285. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220249
补充文件