基于人工智能技术的软件在描述数字乳房造影检查中的性能评估
- 作者: Vasilev Y.A.1,2, Kolsanov A.V.3, Arzamasov K.M.1, Vladzymyrskyy A.V.1,4, Omelyanskaya O.V.1, Semenov S.S.1, Axenova L.E.1
-
隶属关系:
- Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
- National Medical and Surgical Center named after N.I. Pirogov
- Samara State Medical University
- Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
- 期: 卷 5, 编号 4 (2024)
- 页面: 695-711
- 栏目: 原创性科研成果
- URL: https://bakhtiniada.ru/DD/article/view/309830
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD625967
- ID: 309830
如何引用文章
详细
论证。数字乳房造影筛查是早期发现乳腺恶性肿瘤的主要工具,可将死亡率降低20~40%。目前,已开发出许多基于人工智能(AI)的服务来自动分析此类检查。
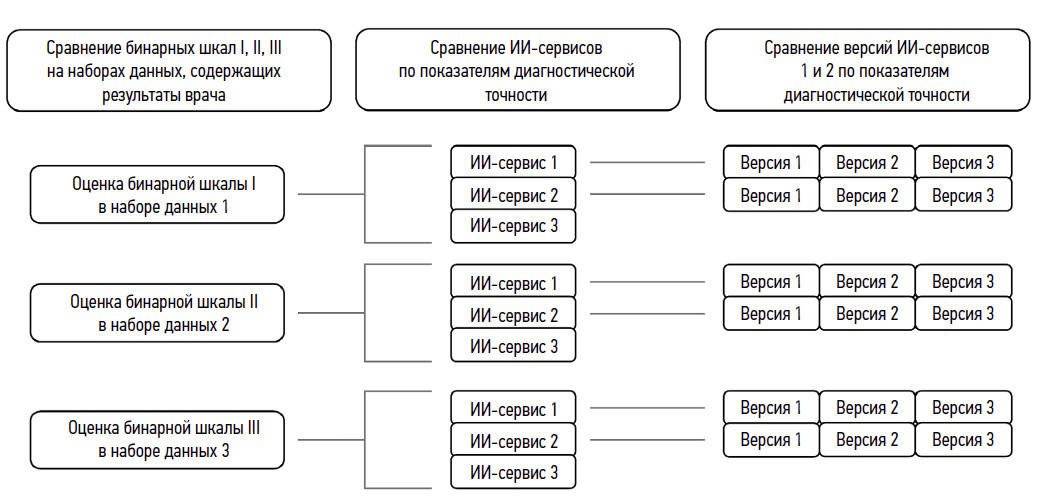
目的 — 比较三种人工智能服务在不同版本中进行的乳房造影检查评估结果与放射科医生的意见。
材料和方法。比较了乳房造影检查二元评估量表与多种类型和版本的AI服务在诊断准确性指标、马修斯系数和最大尤登指数等方面的差异。
结果。比较分析表明,评估数字乳房造影检查的二元评估量表的选择会影响检测到的病理病例数量和AI服务结果的准确性。此外,还发现了诊断准确性指标对阈值的依赖性。版本3中的AI服务1实现了最佳性能,大多数诊断准确性指标都证实了这一点。
结论。我们的研究结果可能有助于选择AI服务来解读乳房造影筛查数据。通过最大化尤登指数来设置AI服务,可以获得灵敏度和特异性的平衡值,但从临床角度来说,并不总是合理的。
作者简介
Yuriy A. Vasilev
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies; National Medical and Surgical Center named after N.I. Pirogov
编辑信件的主要联系方式.
Email: VasilevYA1@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-5283-5961
SPIN 代码: 4458-5608
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine)
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow; MoscowAlexander V. Kolsanov
Samara State Medical University
Email: a.v.kolsanov@samsmu.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-4144-7090
SPIN 代码: 2028-6609
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
俄罗斯联邦, SamaraKirill M. Arzamasov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: ArzamasovKM@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-7786-0349
SPIN 代码: 3160-8062
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine), Head of MIRR Department
俄罗斯联邦, MoscowAnton V. Vladzymyrskyy
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies; Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: VladzimirskijAV@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-2990-7736
SPIN 代码: 3602-7120
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow; MoscowOlga V. Omelyanskaya
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: OmelyanskayaOV@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-0245-4431
SPIN 代码: 8948-6152
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow
Serafim S. Semenov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: SemenovSS3@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-2585-0864
SPIN 代码: 4790-0416
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow
Lubov E. Axenova
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: AksenovaLE@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-0885-1355
SPIN 代码: 7705-6293
俄罗斯联邦, Moscow
参考
- Seely JM, Alhassan T. Screening for breast cancer in 2018-what should we be doing today? Curr Oncol. 2018;25(suppl 1):S115–S124. doi: 10.3747/co.25.3770
- Artificial intelligence in mammography screening. Clinical applications, issues and directions for development [Internet; cited 20 August 2023]. Available from: https://www.itmportal.ru/upload/iblock/69e/7q981uhfaxjhcntal0exngxtq43xeth2/2.2.3. Kandoba ITM_AI-2022.pdf (in Russ.)
- Celsus — AI-software for analysis of X-ray and CT studies. Mammography [Internet; cited 20 Aug 2023]. Available from: https://celsus.ai/productsmammography/
- Kim HE, Kim HH, Han BK, et al. Changes in cancer detection and false positive recall in mammography using artificial intelligence: a retrospective, multireader study. Lancet Digit Health. 2020;2(3):e138–e148. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30003-0
- Yoon JH, Strand F, Baltzer PAT, et al. Standalone AI for Breast Cancer Detection at Screening Digital Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Radiology. 2023;307(5):e222639. doi: 10.1148/radiol.222639
- Zhou X H, Obuchowski NA, McClish DK. Statistical Methods in Diagnostic Medicine. NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2011. doi: 10.1002/9780470906514
- Habibzadeh F, Habibzadeh P, Yadollahie M. On determining the most appropriate test cut off value: the case of tests with continuous results. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2016;26(3):297–307. doi: 10.11613/BM.2016.034
- Schaffter T, Buist DSM, Lee CI, et al. Evaluation of Combined Artificial Intelligence and Radiologist Assessment to Interpret Screening Mammograms. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(3):e200265. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.0265
- McKinney SM, Sieniek M, Godbole V, et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature. 2020;577(7788):89–94. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1799-6
- Nam JG, Kim M, Park J, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm detecting 10 common abnormalities on chest radiographs. Eur Respir J. 2021;57(5):2003061. doi: 10.1183/13993003.03061-2020
- Sakhnov SN, Axenov KD, Axenova LE, et al. Development of a cataract screening model using an open dataset and deep machine learning algorithms. Fyodorov Journal of Ophthalmic Surgery. 2022;(S4):13–20. EDN: VEGPAW doi: 10.25276/0235-4160-2022-4S-13-20
- King G, Zeng L. Logistic Regression in Rare Events Data. Political Analysis. 2001;9(2):137–163. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pan.a004868
- Chen F, Xue Y, Tan MT, Chen P. Efficient statistical tests to compare Youden index: accounting for contingency correlation. Stat Med. 2015;34(9):1560–1576. doi: 10.1002/sim.6432
- Vasiliev YuA, Vladzimirsky AV, Sharova DE, et al. Clinical trials of artificial intelligence systems (radiation diagnostics). Moscow: State budgetary healthcare institution of the city of Moscow «Scientific and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies of the Moscow Health Department». 2023. 40 p. (In Russ.) EDN: PUIJLD
- Arzamasov KM, Vasilev YuA, Vladzymyrskyy AV, et al. The use of computer vision for the mammography preventive research. The Russian Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2023;26(6):117–123. EDN: YBKHPS doi: 10.17116/profmed202326061117
- Vasilev YuA, Tyrov IA, Vladzymyrskyy AV, et al. Double reading mammograms using artificial intelligence technologies: A new model of mass preventive examination organization. Digital Diagnostics. 2023;4(2):93–104. EDN: VRIEOH doi: 10.17816/DD321423
- Vasilev YuA, Tyrov IA, Vladzymyrskyy AV, et al. A New Model of Organizing Mass Screening Based on Stand Alone Artificial Intelligence Used for Fluorography Image Triage. Public Health and Life Environment — PH&LE. 2023;31(11):23-32. EDN: SYIQBX doi: 10.35627/2219-5238/2023-31-11-23-32
- Vladzimirskyy AV, Vasilev YuA, Arzamasov KM, et al. Computer vision in radiology: the first stage of the Moscow experiment. Moscow: Izdatel’skie resheniya; 2022. (In Russ.) EDN: FOYLXK
补充文件