Evaluating the performance of artificial intelligence based software for digital mammography characterization
- Авторлар: Vasilev Y.A.1,2, Kolsanov A.V.3, Arzamasov K.M.1, Vladzymyrskyy A.V.1,4, Omelyanskaya O.V.1, Semenov S.S.1, Axenova L.E.1
-
Мекемелер:
- Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
- National Medical and Surgical Center named after N.I. Pirogov
- Samara State Medical University
- Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
- Шығарылым: Том 5, № 4 (2024)
- Беттер: 695-711
- Бөлім: Original Study Articles
- URL: https://bakhtiniada.ru/DD/article/view/309830
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD625967
- ID: 309830
Дәйексөз келтіру
Аннотация
BACKGROUND: Digital screening mammography is a key modality for early detection of breast cancer, reducing mortality by 20–40%. Many artificial intelligence (AI)-based services have been developed to automate the analysis of imaging data.
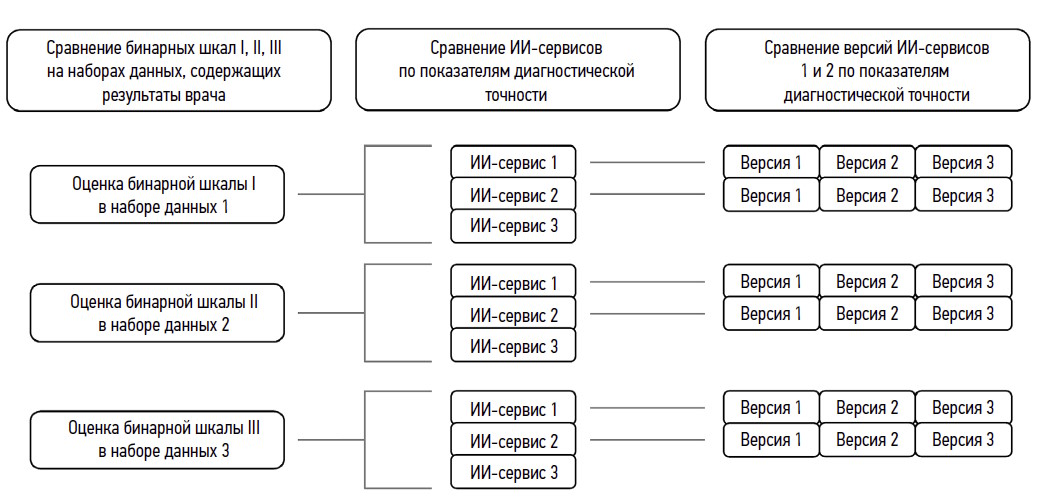
AIM: The aim of the study was to compare mammography assessments using three types of AI services in multiple versions with radiologists’ conclusions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Binary mammography scoring scales were compared with several types and versions of AI services regarding diagnostic accuracy, Matthews correlation coefficient, and maximum Youden’s index.
RESULTS: A comparative analysis showed that the use of a binary scale for evaluating digital mammography affects the number of detected abnormalities and accuracy of AI results. In addition, diagnostic accuracy was found to be threshold dependent. AI Service 1 in version 3 had the best performance, as confirmed by most diagnostic accuracy parameters.
CONCLUSIONS: Our results can be used to select AI services for interpreting mammography screening data. Using Youden’s index maximization to set up an AI service provides a balance of sensitivity and specificity that is not always clinically relevant.
Толық мәтін
##article.viewOnOriginalSite##Авторлар туралы
Yuriy Vasilev
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies; National Medical and Surgical Center named after N.I. Pirogov
Хат алмасуға жауапты Автор.
Email: VasilevYA1@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-5283-5961
SPIN-код: 4458-5608
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine)
Ресей, Moscow; MoscowAlexander Kolsanov
Samara State Medical University
Email: a.v.kolsanov@samsmu.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-4144-7090
SPIN-код: 2028-6609
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
Ресей, SamaraKirill Arzamasov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: ArzamasovKM@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-7786-0349
SPIN-код: 3160-8062
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine), Head of MIRR Department
Ресей, MoscowAnton Vladzymyrskyy
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies; Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: VladzimirskijAV@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-2990-7736
SPIN-код: 3602-7120
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
Ресей, Moscow; MoscowOlga Omelyanskaya
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: OmelyanskayaOV@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-0245-4431
SPIN-код: 8948-6152
Ресей, Moscow
Serafim Semenov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: SemenovSS3@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-2585-0864
SPIN-код: 4790-0416
Ресей, Moscow
Lubov Axenova
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: AksenovaLE@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-0885-1355
SPIN-код: 7705-6293
Ресей, Moscow
Әдебиет тізімі
- Seely JM, Alhassan T. Screening for breast cancer in 2018-what should we be doing today? Curr Oncol. 2018;25(suppl 1):S115–S124. doi: 10.3747/co.25.3770
- Artificial intelligence in mammography screening. Clinical applications, issues and directions for development [Internet; cited 20 August 2023]. Available from: https://www.itmportal.ru/upload/iblock/69e/7q981uhfaxjhcntal0exngxtq43xeth2/2.2.3. Kandoba ITM_AI-2022.pdf (in Russ.)
- Celsus — AI-software for analysis of X-ray and CT studies. Mammography [Internet; cited 20 Aug 2023]. Available from: https://celsus.ai/productsmammography/
- Kim HE, Kim HH, Han BK, et al. Changes in cancer detection and false positive recall in mammography using artificial intelligence: a retrospective, multireader study. Lancet Digit Health. 2020;2(3):e138–e148. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30003-0
- Yoon JH, Strand F, Baltzer PAT, et al. Standalone AI for Breast Cancer Detection at Screening Digital Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. Radiology. 2023;307(5):e222639. doi: 10.1148/radiol.222639
- Zhou X H, Obuchowski NA, McClish DK. Statistical Methods in Diagnostic Medicine. NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2011. doi: 10.1002/9780470906514
- Habibzadeh F, Habibzadeh P, Yadollahie M. On determining the most appropriate test cut off value: the case of tests with continuous results. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2016;26(3):297–307. doi: 10.11613/BM.2016.034
- Schaffter T, Buist DSM, Lee CI, et al. Evaluation of Combined Artificial Intelligence and Radiologist Assessment to Interpret Screening Mammograms. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(3):e200265. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.0265
- McKinney SM, Sieniek M, Godbole V, et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature. 2020;577(7788):89–94. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1799-6
- Nam JG, Kim M, Park J, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm detecting 10 common abnormalities on chest radiographs. Eur Respir J. 2021;57(5):2003061. doi: 10.1183/13993003.03061-2020
- Sakhnov SN, Axenov KD, Axenova LE, et al. Development of a cataract screening model using an open dataset and deep machine learning algorithms. Fyodorov Journal of Ophthalmic Surgery. 2022;(S4):13–20. EDN: VEGPAW doi: 10.25276/0235-4160-2022-4S-13-20
- King G, Zeng L. Logistic Regression in Rare Events Data. Political Analysis. 2001;9(2):137–163. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pan.a004868
- Chen F, Xue Y, Tan MT, Chen P. Efficient statistical tests to compare Youden index: accounting for contingency correlation. Stat Med. 2015;34(9):1560–1576. doi: 10.1002/sim.6432
- Vasiliev YuA, Vladzimirsky AV, Sharova DE, et al. Clinical trials of artificial intelligence systems (radiation diagnostics). Moscow: State budgetary healthcare institution of the city of Moscow «Scientific and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies of the Moscow Health Department». 2023. 40 p. (In Russ.) EDN: PUIJLD
- Arzamasov KM, Vasilev YuA, Vladzymyrskyy AV, et al. The use of computer vision for the mammography preventive research. The Russian Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2023;26(6):117–123. EDN: YBKHPS doi: 10.17116/profmed202326061117
- Vasilev YuA, Tyrov IA, Vladzymyrskyy AV, et al. Double reading mammograms using artificial intelligence technologies: A new model of mass preventive examination organization. Digital Diagnostics. 2023;4(2):93–104. EDN: VRIEOH doi: 10.17816/DD321423
- Vasilev YuA, Tyrov IA, Vladzymyrskyy AV, et al. A New Model of Organizing Mass Screening Based on Stand Alone Artificial Intelligence Used for Fluorography Image Triage. Public Health and Life Environment — PH&LE. 2023;31(11):23-32. EDN: SYIQBX doi: 10.35627/2219-5238/2023-31-11-23-32
- Vladzimirskyy AV, Vasilev YuA, Arzamasov KM, et al. Computer vision in radiology: the first stage of the Moscow experiment. Moscow: Izdatel’skie resheniya; 2022. (In Russ.) EDN: FOYLXK
Қосымша файлдар