Bone mineral density radiopaque templates for cone beam computed tomography and multidetector computed tomography
- Authors: Hossain S.D.1, Petraikin A.V.2, Muraev A.A.1, Danaev A.B.3, Burenchev D.V.2, Dolgalev A.A.3, Vasilev Y.A.2, Sharova D.E.2, Ivanov S.Y.1,4
-
Affiliations:
- Peoples Friendship University of Russia
- Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
- Stavropol State Medical University
- The First Sechenov Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University)
- Issue: Vol 4, No 3 (2023)
- Pages: 292-305
- Section: Original Study Articles
- URL: https://bakhtiniada.ru/DD/article/view/254070
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD501771
- ID: 254070
Cite item
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Cone beam computed tomography is widely applied for diagnostics and planning various manipulations in the maxillofacial region, for example, dental implantation. Its advantages include high spatial resolution, low radiation exposure, and cost-effectiveness. However, it has a significant drawback: the inability to determine the density of the jaw bone in Hounsfield Units (HU).
AIMS: This study aimed to develop radiopaque templates with sets of X-ray density based on potassium hydrophosphate and beta-tricalcium phosphate, to study templates on various cone beam computed tomography and multidetector computed tomography devices, and to determine a cross-calibration algorithm for assessing the bone mineral density of the jaw in HU.
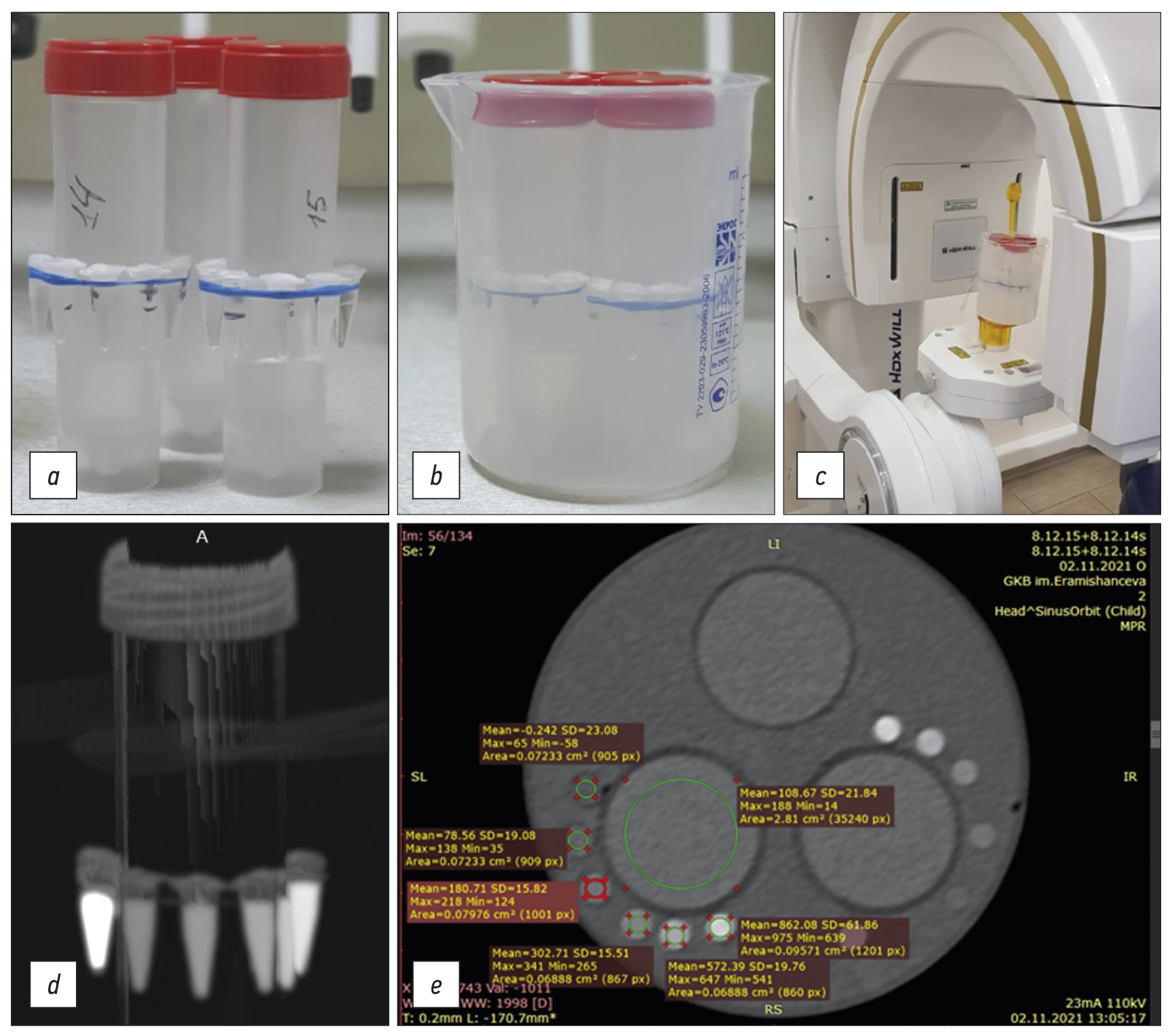
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The bone mineral density template comprised microtubes (0.25 ml) with potassium hydrophosphate concentrations of 49.96, 99.98, 174.99, 349.99, and 549.98 mg/ml, and a suspension of beta-tricalcium phosphate with an equivalent concentration of potassium hydrophosphate 1,506 mg/ml, designed to simulate the types of bone density according to C. Mish. The study was carried out on two multidetector computed tomography and four cone beam computed tomography machines. Cross-calibration was referred on the “standard” multidetector computed tomography 1 mode 120 kV, 200 mA.
RESULTS: There was a significant scatter of the X-ray values (HU for multidetector computed tomography and GV for cone beam computed tomography) vs. bone mineral density, with varying slopes, bias, and curve shapes. After cross-calibration, good comparability corresponding to the multidetector computed tomography 1 mode was shown. The median of the differences before cross-calibration was 160 relative units (HU, GV), after decreased by 10 times and amounted to 16 rel. units (p=0.000). The mean difference for cone beam computed tomography was significantly higher (30 rel. units) than for multidetector computed tomography (8 rel. units) (p=0.024, Mann–Whitney U test).
CONCLUSION: The developed radiopaque template enables the standardization of densitometric indicators for cone beam computed tomography and various multidetector computed tomography modes. On average, the spread after cross-calibration is reduced by 10 times, which makes it possible to classify bone tissue in HU according to C. Mish.
Full Text
##article.viewOnOriginalSite##About the authors
Shazmim D. Hossain
Peoples Friendship University of Russia
Email: shazmim@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-5410-1849
Assistant Lecturer
Russian Federation, MoscowAlexey V. Petraikin
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Author for correspondence.
Email: alexeypetraikin@gmail.com
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-1694-4682
SPIN-code: 6193-1656
MD, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Assistant Professor, Chief Researcher
Russian Federation, MoscowAlexandr A. Muraev
Peoples Friendship University of Russia
Email: muraev_aa@pfur.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-3982-5512
SPIN-code: 1431-5936
MD, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Professor
Russian Federation, MoscowAslan B. Danaev
Stavropol State Medical University
Email: aslandanaev111@mail.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-4754-3101
SPIN-code: 7266-7722
Assistant Lecturer
Russian Federation, StavropolDmitry V. Burenchev
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: BurenchevDV@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-2894-6255
SPIN-code: 2411-3959
MD, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Chief Researcher
Russian Federation, MoscowAlexander A. Dolgalev
Stavropol State Medical University
Email: dolgalev@dolgalev.pro
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-6352-6750
SPIN-code: 5941-5771
MD, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Assistant Professor
Russian Federation, StavropolYuriy A. Vasilev
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: VasilevYA1@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-0208-5218
SPIN-code: 4458-5608
MD, Cand. Sci. (Med.)
Russian Federation, MoscowDarya E. Sharova
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: SharovaDE@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-5792-3912
SPIN-code: 1811-7595
Russian Federation, Moscow
Sergey Yu. Ivanov
Peoples Friendship University of Russia; The First Sechenov Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University)
Email: syivanov@yandex.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-5458-0192
SPIN-code: 2607-2679
MD, Dr. Sci. (Med.), Professor, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Russian Federation, Moscow; MoscowReferences
- Hounsfield GN. Computerized transverse axial scanning (tomography). Description of system. Br J Radiol. 1973;46(552): 1016–1022. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-46-552-1016
- Bornstein MM, Scarfe WC, Vaughn VM, Jacobs R. Cone beam computed tomography in implant dentistry: A systematic review focusing on guidelines, indications, and radiation dose risks. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(Suppl):55–77. doi: 10.11607/jomi.2014suppl.g1.4
- DenOtter TD, Schubert J. Hounsfield Unit. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Kim Y, Oh TJ, Misch CE, Wang HL. Occlusal considerations in implant therapy: Clinical guidelines with biomechanical rationale. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2005;16(1):26–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2004.01067.x
- Woelber JP, Fleiner J, Rau J, et al. Accuracy and usefulness of CBCT in periodontology: A systematic review of the literature. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2018;38(2):289–297. doi: 10.11607/prd.2751
- Song D, Shujaat S, de Faria Vasconcelos K, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of CBCT versus intraoral imaging for assessment of peri-implant bone defects. BMC Med Imaging. 2021;21(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00557-9
- Savoldi F, Yon MJ, Kwok VM, et al. Accuracy of CBCT in the identification of mental, lingual, and retromolar foramina: A comparison with visual inspection of human dry mandibles. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41(6):e277–e286. doi: 10.11607/prd.4770
- Levi C, Gray JE, McCullough EC, Hattery RR. The unreliability of CT numbers as absolute values. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982;139(3): 443–447. doi: 10.2214/ajr.139.3.443
- Petraikin AV, Skripnikova IA. Quantitative computed tomography, modern data. Review. Medical Imaging. 2021;25(4):134–146. (In Russ). doi: 10.24835/1607-0763-1049
- Ivanov DV, Kirillova IV, Kossovich LY, et al. Influence of convolution kernel and beam-hardening effect on the assessment of trabecular bonemineral density using quantitative computed tomography. News Saratov University. 2020;20(2):205–219. (In Russ). doi: 10.18500/1816-9791-2020-20-2-205-219
- Petraikin AV, Smorchkova AK, Kudryavtsev ND, et al. Comparison of two asynchronous QCT methods. Medical Imaging. 2020;24(4): 108–118. (In Russ). doi: 10.24835/1607-0763-2020-4-108-118
- Witt RM, Cameron JR. Bone Standards. USAEC Progress Report No. COO-1422-42 US Atomic Energy Comission, Madison, Wisconsin; 1969.
- Cann CE, Genant HK. Precise measurement of vertebral mineral content using computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1980;4(4):493–500. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198008000-00018
- Hubbell JH. Photon cross sections, attenuation coefficients, and energy absorption coefficients from 10 keV to 100 GeV. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD; 1969. doi: 10.6028/NBS.NSRDS.29
- International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU). Tissue Substitutes in Radiation Dosimetry and Measurement. ICRU Report.1989;(44):1–189.
- Nikolaev AE, Korkunova OA, Blokhin IA, et al. Calcification density oncomputed tomography depending on scanning parameters: Phantom study. (In Russ). Med Imaging. 2020;24(4):119–132. doi: 10.24835/1607-0763-2020-4-119-132
- Gaur A, Dhillon M, Puri N, et al. Questionable accuracy of CBCT in determining bone density: A comparative CBCT-CT in vitro study. Dent Med Probl. 2022;59(3):413–419. doi: 10.17219/dmp/143504
- Martinez C, de Molina C, Desco M, Abella M. Optimization of a calibration phantom for quantitative radiography. Med Phys. 2021;48(3):1039–1053. doi: 10.1002/mp.14638
- Hu Z, Wang T, Pan X, et al. Comparison of diagnosis of cracked tooth using contrast-enhanced CBCT and micro-CT. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2021;50(7):20210003. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20210003
- Lehmann L, Alvarez R, Macovski A, et al. Generalized image combinations in dual KVP digital radiography. Med Phys. 1981;8(5):659–667. doi: 10.1118/1.595025
- Chuang KS, Huang H. Comparison of four dual energy image decomposition methods. Physics Med Biol. 1988;33(4):455. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/33/4/005
- Gingold EL, Hasegawa BH. Systematic bias in basis material decomposition applied to quantitative dual-energy X-ray imaging. Med Phys. 1992;19(1):25–33. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/33/4/005
- Cardinal HN, Fenster A. An accurate method for direct dual-energy calibration and decomposition. Med Phys. 1990;17(3):327–341. doi: 10.1118/1.596512
- Jacobs R, Salmon B, Codari M, et al. Cone beam computed tomography in implant dentistry: recommendations for clinical use. BMC Oral Health. 2018;18(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12903-018-0523-5
- Dolgalev AA, Danaev AB, Yusupov RD, et al. Objective assessment of measurement error in significant cone-beam computed tomography in dental practice. Med Alphabet. 2022;(7):65–68. (In Russ). doi: 10.33667/2078-5631-2022-7-65-68
- Cassetta M, Stefanelli LV, Di Carlo S, et al. The accuracy of CBCT in measuring jaws bone density. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16(10):1425–1429.
- Harvey S, Patel S. Guidelines and template for reporting on CBCT scans. Br Dent J. 2020;228(1):15–18. doi: 10.1038/s41415-019-1115-8
- Cassetta M, Stefanelli LV, Pacifici A, et al. How accurate is CBCT in measuring bone density? A comparative CBCT-CT in vitro study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2014;16(4):471–478. doi: 10.1111/cid.12027
- Parsa A, Ibrahim N, Hassan B, et al. Bone quality evaluation at dental implant site using multislice CT, micro-CT, and cone beam CT. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(1):e1–7. doi: 10.1111/clr.12315
- Van Dessel J, Nicolielo LF, Huang Y, et al. Accuracy and reliability of different cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) devices for structural analysis of alveolar bone in comparison with multislice CT and micro-CT. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2017;10(1):95–105.
- Dillenseger JP, Matern JF, Gros CI, et al. MSCT versus CBCT: Evaluation of high-resolution acquisition modes for dento-maxillary and skull-base imaging. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(2):505–515. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3439-8
- Schegerer AA, Lechel U, Ritter M, et al. Dose and image quality of cone-beam computed tomography as compared with conventional multislice computed tomography in abdominal imaging. Invest Radiol. 2014;49(10):675–684. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000069
- Veldhoen S, Schöllchen M, Hanken H, et al. Performance of cone-beam computed tomography and multidetector computed tomography in diagnostic imaging of the midface: A comparative study on Phantom and cadaver head scans. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(2):790–800. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4387-2
- Grunz JP, Weng AM, Gietzen CH, et al. Evaluation of ultra-high-resolution cone-beam CT prototype of twin robotic radiography system for cadaveric wrist imaging. Acad Radiol. 202;28(10):e314–e322. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.06.018
- Medelnik J, Hertrich K, Steinhäuser-Andresen S, et al. Accuracy of anatomical landmark identification using different CBCT- and MSCT-based 3D images: An in vitro study. J Orofac Orthop. 2011;72(4):261–278. doi: 10.1007/s00056-011-0032-5
- Elshenawy H, Aly W, Salah N, et al. Influence of small, midi, medium and large fields of view on accuracy of linear measurements in CBCT imaging: Diagnostic accuracy study. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019;7(6):1037–1041. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.232
Supplementary files