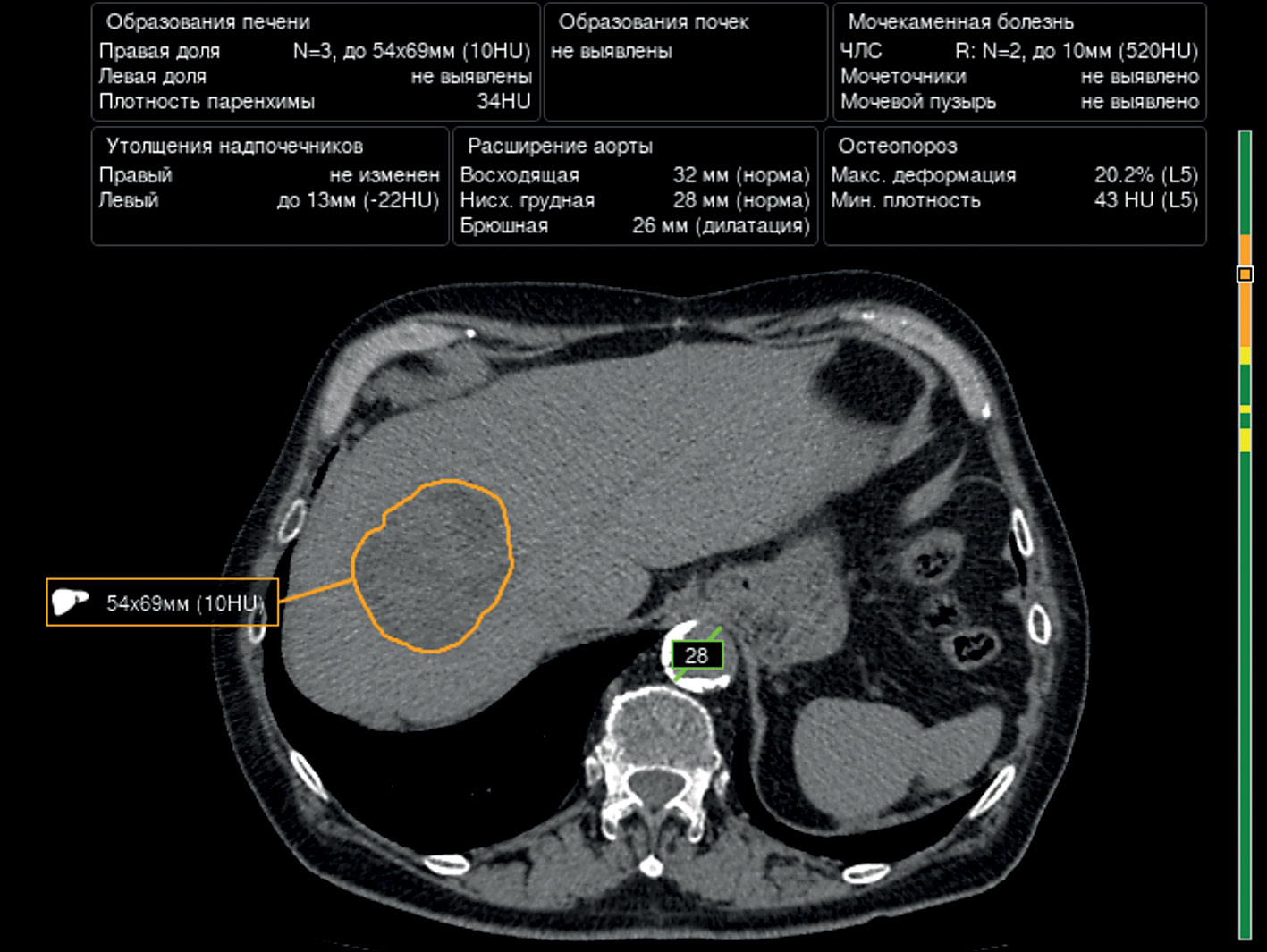
Prospects of using computer vision technology to detect urinary stones and liver and kidney neoplasms on computed tomography images of the abdomen and retroperitoneal space
- Authors: Vasilev Y.A.1,2, Vladzymyrskyy A.V.1,3, Arzamasov K.M.1, Shikhmuradov D.U.1, Pankratov A.V.1, Ulyanov I.V.1, Nechaev N.B.1
-
Affiliations:
- Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
- National Medical and Surgical Center Named after N.I. Pirogov
- I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
- Issue: Vol 5, No 1 (2024)
- Pages: 101-119
- Section: Reviews
- URL: https://bakhtiniada.ru/DD/article/view/262980
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17816/DD515814
- ID: 262980
Cite item
Abstract
The article presents a selective literature review on the use of computer vision algorithms for the diagnosis of liver and kidney neoplasms and urinary stones using computed tomography images of the abdomen and retroperitoneal space. The review included articles published between January 1, 2020, and April 24, 2023. Pixel-based algorithms showed the greatest diagnostic accuracy parameters for segmenting the liver and its neoplasms (accuracy, 99.6%; Dice similarity coefficient, 0.99). Voxel-based algorithms were superior at classifying liver neoplasms (accuracy, 82.5%). Pixel- and voxel-based algorithms fared equally well in segmenting kidneys and their neoplasms, as well as classifying kidney tumors (accuracy, 99.3%; Dice similarity coefficient, 0.97). Computer vision algorithms can detect urinary stones measuring 3 mm or larger with a high degree of accuracy of up to 93.0%. Thus, existing computer vision algorithms not only effectively detect liver and kidney neoplasms and urinary stones but also accurately determine their quantitative and qualitative characteristics. Evaluating voxel data improves the accuracy of neoplasm type determination since the algorithm analyzes the neoplasm in three dimensions rather than only the plane of one slice.
Full Text
##article.viewOnOriginalSite##About the authors
Yuriy A. Vasilev
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies; National Medical and Surgical Center Named after N.I. Pirogov
Email: npcmr@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-0208-5218
SPIN-code: 4458-5608
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine)
Russian Federation, Moscow; MoscowAnton V. Vladzymyrskyy
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies; I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University
Email: VladzimirskijAV@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-2990-7736
SPIN-code: 3602-7120
MD, Dr. Sci. (Medicine), Professor
Russian Federation, Moscow; MoscowKirill M. Arzamasov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: ArzamasovKM@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0001-7786-0349
SPIN-code: 3160-8062
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine)
Russian Federation, MoscowDavid U. Shikhmuradov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: ShikhmuradovDU@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0003-1597-5786
SPIN-code: 9641-0913
MD
Russian Federation, MoscowAndrey V. Pankratov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: PankratovAV3@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0009-0008-4741-4530
MD
Russian Federation, MoscowIliya V. Ulyanov
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Email: UlyanovIV2@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0000-0002-8330-6069
SPIN-code: 5898-3242
MD
Russian Federation, MoscowNikolay B. Nechaev
Research and Practical Clinical Center for Diagnostics and Telemedicine Technologies
Author for correspondence.
Email: NechaevNB@zdrav.mos.ru
ORCID iD: 0009-0007-9219-7726
SPIN-code: 3232-1545
MD, Cand. Sci. (Medicine)
Russian Federation, MoscowReferences
- Iliashenko OY, Lukyanchenko EL. Possibilities of using computer vision for data analytics in medicine. Izvestiya of Saratov University. Mathematics. Mechanics. Informatics. 2022;22(2):224–232. EDN: MCSLKQ doi: 10.18500/1816-9791-2022-22-2-224-232
- Alekseeva MG, Zubov AI, Novikov MYu. Artificial intelligence in medicine. Meždunarodnyj naučno-issledovatelʹskij žurnal. 2022;7(121):10–13. EDN: JMMMDF doi: 10.23670/IRJ.2022.121.7.038
- Gusev AV, Vladzymyrskyy AV, Sharova DE, Arzamasov KM, Khramov AE. Evolution of research and development in the field of artificial intelligence technologies for healthcare in the Russian Federation: results of 2021. Digital Diagnostics. 2022;3(3):178–194. EDN: KHWQWZ doi: 10.17816/DD107367
- Wang L, Wang H, Huang Y, et al. Trends in the application of deep learning networks in medical image analysis: Evolution between 2012 and 2020. Eur J Radiol. 2022;146:110069. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.110069
- Alrefai N, Ibrahim O. AI Deep learning-based cancer classification for microarray data: A systematic review. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology. 2021;99:2312–2332. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.6126510
- Clinical trials of artificial intelligence systems (radiation diagnostics). Vasil’ev YuA, Vladzymyrskyy AV, Sharova DE, editors. Moscow: GBUZ «NPKTs DiT DZM»; 2023. EDN: PUIJLD
- Lee J, Kim KW, Kim SY, et al. Automatic detection method of hepatocellular carcinomas using the non-rigid registration method of multi-phase liver CT images. J Xray Sci Technol. 2015;23(3):275–288. doi: 10.3233/XST-150487
- Patel BN, Boltyenkov AT, Martinez MG, et al. Cost-effectiveness of dual-energy CT versus multiphasic single-energy CT and MRI for characterization of incidental indeterminate renal lesions. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020;45(6):1896–1906. doi: 10.1007/s00261-019-02380-x
- Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, et al. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;68(2):723–750. doi: 10.1002/hep.29913
- Ayuso C, Rimola J, Vilana R, et al. Diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): current guidelines. Eur J Radiol. 2018;101:72–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.01.025
- Liver cancer (hepatocellular). Clinical guidelines. ID 1. Approved by the Scientific and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. 2022. Available from: https://cr.minzdrav.gov.ru/schema/1_3 (In Russ)
- Rahman H, Bukht TFN, Imran A, et al. A Deep Learning Approach for Liver and Tumor Segmentation in CT Images Using ResUNet. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(8):368. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9080368
- Maqsood M, Bukhari M, Ali Z, et al. A Residual-Learning-Based Multi-Scale Parallel-Convolutions- Assisted Efficient CAD System for Liver Tumor Detection. Mathematics. 2021;9(10):1133. doi: 10.3390/math9101133
- Khan RA, Luo Y, Wu FX. RMS-UNet: Residual multi-scale UNet for liver and lesion segmentation. Artif Intell Med. 2022;124:102231. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2021.102231
- Affane A, Kucharski A, Chapuis P, et al. Segmentation of Liver Anatomy by Combining 3D U-Net Approaches. Applied Sciences. 2021;11(11):4895. doi: 10.3390/app11114895
- Han X, Wu X, Wang S, et al. Automated segmentation of liver segment on portal venous phase MR images using a 3D convolutional neural network. Insights Imaging. 2022;13(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13244-022-01163-1
- Wang J, Zhang X, Guo L, et al. Multi-scale attention and deep supervision-based 3D UNet for automatic liver segmentation from CT. Math Biosci Eng. 2023;20(1):1297–1316. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2023059
- Kashala KG, Song Y, Liu Z. Optimization of FireNet for Liver Lesion Classification. Electronics. 2020;9(8):1237. doi: 10.3390/electronics9081237
- Trivizakis E, Manikis GC, Nikiforaki K, et al. Extending 2-D Convolutional Neural Networks to 3-D for Advancing Deep Learning Cancer Classification With Application to MRI Liver Tumor Differentiation. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019;23(3):923–930. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2886276
- Zhou J, Wang W, Lei B, et al. Automatic Detection and Classification of Focal Liver Lesions Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks: A Preliminary Study. Front Oncol. 2021;10:581210. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.581210
- Rela M, Rao SN, Patil RR. Performance analysis of liver tumor classification using machine learning algorithms. International Journal of Advanced Technology and Engineering Exploration. 2022;9(86):143–154. doi: 10.19101/IJATEE.2021.87465
- Oberai A, Varghese B, Cen S, et al. Deep learning based classification of solid lipid-poor contrast enhancing renal masses using contrast enhanced CT. Br J Radiol. 2020;93(1111):20200002. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200002
- Lin Z, Cui Y, Liu J, et al. Automated segmentation of kidney and renal mass and automated detection of renal mass in CT urography using 3D U-Net-based deep convolutional neural network. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(7):5021–5031. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07608-9
- Toda N, Hashimoto M, Arita Y, et al. Deep Learning Algorithm for Fully Automated Detection of Small (≤4 cm) Renal Cell Carcinoma in Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Using a Multicenter Database. Invest Radiol. 2022;57(5):327–333. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000842
- Ding Y, Chen Z, Wang Z, et al. Three-dimensional deep neural network for automatic delineation of cervical cancer in planning computed tomography images. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2022;23(4):e13566. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13566
- Zhu XL, Shen HB, Sun H, et al. Improving segmentation and classification of renal tumors in small sample 3D CT images using transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2022;17(7):1303–1311. doi: 10.1007/s11548-022-02587-2
- Hsiao CH, Sun TL, Lin PC, et al. A deep learning-based precision volume calculation approach for kidney and tumor segmentation on computed tomography images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;221:106861. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106861
- Hsiao CH, Lin PC, Chung LA, et al. A deep learning-based precision and automatic kidney segmentation system using efficient feature pyramid networks in computed tomography images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;221:106854. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106854
- Islam MN, Hasan M, Hossain MK, et al. Vision transformer and explainable transfer learning models for auto detection of kidney cyst, stone and tumor from CT-radiography. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11440. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15634-4
- Yang L, Gao L, Arefan D, et al. A CT-based radiomics model for predicting renal capsule invasion in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Med Imaging. 2022;22(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00741-5
- Shehata M, Alksas A, Abouelkheir RT, et al. A Comprehensive Computer-Assisted Diagnosis System for Early Assessment of Renal Cancer Tumors. Sensors (Basel). 2021;21(14):4928. doi: 10.3390/s21144928
- Kulikovskiy VF, Shkodkin SV, Batishchev SA, et al. Modern research and thinking about the epidemiology and pathogenesis of urolithiasis. Nauchnyi rezul’tat. Meditsina i farmatsiya. 2016;2(4):4–12. EDN: NSGAXL doi: 10.18413/2313-8955-2016-2-4-4-12
- Gadzhiev N, Prosyannikov M, Malkhasyan V, et al. Urolithiasis prevalence in the Russian Federation: analysis of trends over a 15-year period. World J Urol. 2021.Vol. 39(10):3939–3944. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03729-y
- Urology. Russian Clinical Recommendations. Alyaev YuG, Glybochko PV, Pushkar’ DYu, editors. Moscow: GEOTARMedia; 2016. (In Russ).
- Caglayan A, Horsanali MO, Kocadurdu K, et al. Deep learning model-assisted detection of kidney stones on computed tomography. Int Braz J Urol. 2022;48(5):830–839. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2022.0132
- Elton DC, Turkbey EB, Pickhardt PJ, Summers RM. A deep learning system for automated kidney stone detection and volumetric segmentation on noncontrast CT scans. Med Phys. 2022;49(4):2545–2554. doi: 10.1002/mp.15518
- He Z, An L, Chang Z, Wu W. Comment on “Deep learning computer vision algorithm for detecting kidney stone composition”. World J Urol. 2021;39(1):291. doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03181-4
- Doyle PW, Kavoussi NL. Machine learning applications to enhance patient specific care for urologic surgery. World J Urol. 2022;40(3):679–686. doi: 10.1007/s00345-021-03738-x
- Neymark AI, Neymark BA, Ershov AV, et al. The use of intelligent analysis (IA) in determining the tactics of treating patients with nephrolithiasis. Urologia Journal. 2023;(3915603231162881). doi: 10.1177/03915603231162881
- Kadlec AO, Ohlander S, Hotaling J, et al. Nonlinear logistic regression model for outcomes after endourologic procedures: a novel predictor. Urolithiasis. 2014;42(4):323–330. doi: 10.1007/s00240-014-0656-1
- Black KM, Law H, Aldoukhi A, et al. Deep learning computer vision algorithm for detecting kidney stone composition. BJU Int. 2020;125(6):920–924. doi: 10.1111/bju.15035
- Zhang GM, Sun H, Xue HD, et al. Prospective prediction of the major component of urinary stone composition with dual-source dual-energy CT in vivo. Clin Radiol. 2016;71(11):1178–1183. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2016.07.012
- Chaytor RJ, Rajbabu K, Jones PA, McKnight L. Determining the composition of urinary tract calculi using stone-targeted dual-energy CT: evaluation of a low-dose scanning protocol in a clinical environment. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1067):20160408. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160408
- Kapanadze LB, Serova NS, Rudenko VI. Application of dual-energy computer tomography in diagnostics of urolithiasis. REJR. 2017;7(3):165–173. EDN: ZWBLYL doi: 10.21569/2222-7415-2017-7-3-165-173
- Cui Y, Sun Z, Ma S, et al. Automatic Detection and Scoring of Kidney Stones on Noncontrast CT Images Using S.T.O.N.E. Nephrolithometry: Combined Deep Learning and Thresholding Methods. Mol Imaging Biol. 2021;23(3):436–445. doi: 10.1007/s11307-020-01554-0
- Okhunov Z, Friedlander JI, George AK, et al. S.T.O.N.E. nephrolithometry: novel surgical classification system for kidney calculi. Urology. 2013;81(6):1154–1159. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2012.10.083
- Yildirim K, Bozdag PG, Talo M, et al. Deep learning model for automated kidney stone detection using coronal CT images. Comput Biol Med. 2021;135:104569. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104569
- Kodenko MR, Reshetnikov RV, Makarova TA. Modification of quality assessment tool for artificial intelligence diagnostic test accuracy studies (QUADAS-CAD). Digital Diagnostics. 2022;3(1S):4–5. EDN: KNBHOJ doi: 10.17816/DD105567
- Schwartz FR, Clark DP, Ding Y, Ramirez-Giraldo JC. Evaluating renal lesions using deep-learning based extension of dual-energy FoV in dual-source CT-A retrospective pilot study. Eur J Radiol. 2021;139:109734. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109734
- Li W, Diao K, Wen Y, et al. High-strength deep learning image reconstruction in coronary CT angiography at 70-kVp tube voltage significantly improves image quality and reduces both radiation and contrast doses. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(5):2912–2920. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08424-5
- Bae JS, Lee JM, Kim SW, et al. Low-contrast-dose liver CT using low monoenergetic images with deep learning-based denoising for assessing hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled noninferiority trial. Eur Radiol. 2023;33(6):4344–4354. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09298-x
Supplementary files